How a Photovoltaic Cell Receives Energy Input

Introduction
When it comes to renewable energy sources, photovoltaic cells are at the forefront of innovation. These cells convert sunlight into electricity, providing a sustainable and environmentally friendly power source. But how exactly does a photovoltaic cell receive energy input? In this article, we will explore the process in detail.
Understanding Photovoltaic Cells
Before delving into how a photovoltaic cell receives energy input, it’s important to understand how these cells work. Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are made of semiconductor materials that have the ability to convert light into electricity. When sunlight hits the cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating an electric current.
The Role of Sunlight
The primary source of energy input for a photovoltaic cell is sunlight. Sunlight is composed of photons, which are particles of light that carry energy. When sunlight reaches the photovoltaic cell, the photons penetrate the cell’s semiconductor material, causing the electrons to become energized and creating an electric current. The amount of energy input received by the cell is directly related to the intensity of sunlight and the surface area of the cell.
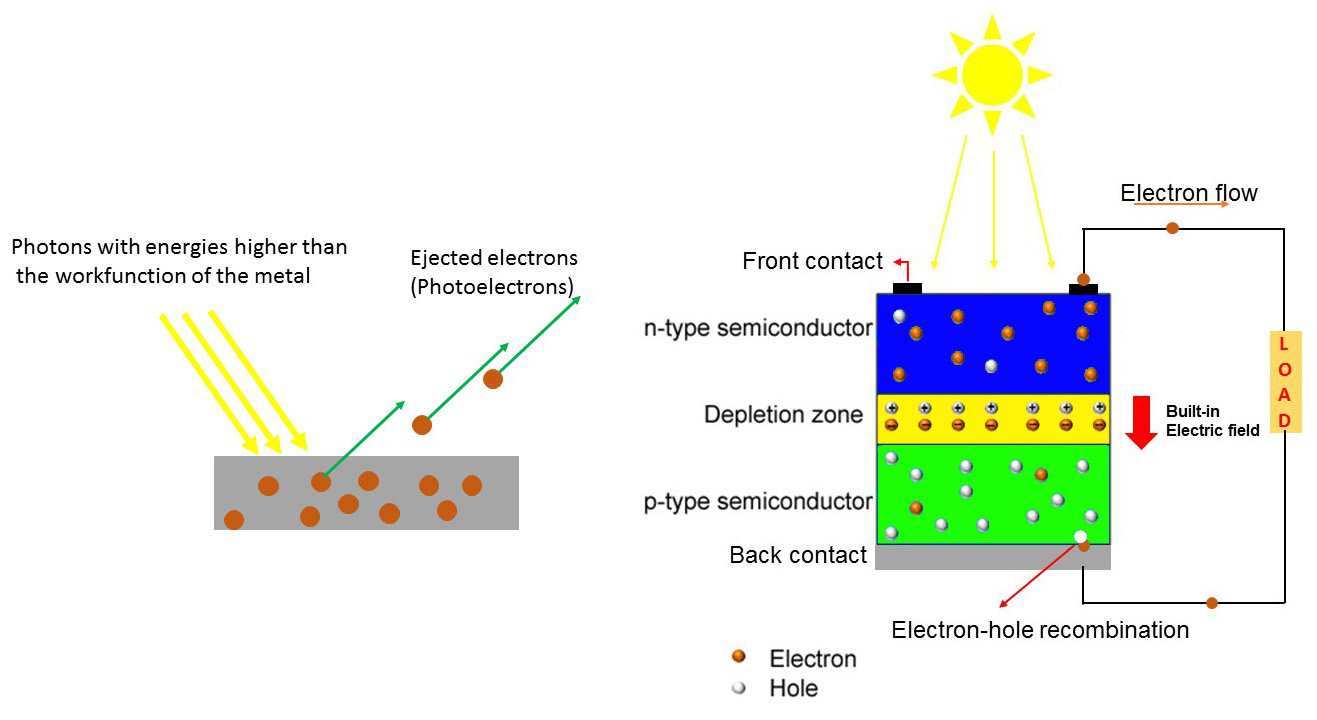
The Function of the Semiconductor Material
The semiconductor material within the photovoltaic cell plays a crucial role in receiving energy input. Typically made of silicon, the semiconductor material is carefully engineered to have specific properties that allow it to efficiently capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. The material’s ability to create a flow of electrons when exposed to sunlight is what enables the photovoltaic cell to generate electricity.
The Photovoltaic Cell Structure
In order to effectively receive energy input, photovoltaic cells are designed with a specific structure. The cell is composed of multiple layers, each with a distinct function. The top layer is made of a transparent material that allows sunlight to pass through to the semiconductor layer. Beneath the semiconductor layer is a metal backing that collects the electric current generated by the excited electrons.
The Role of the P-N Junction
At the heart of the photovoltaic cell’s structure is the p-n junction, where the n-type and p-type semiconductor materials meet. This junction is where the magic happens – when sunlight energizes the electrons, the p-n junction facilitates the flow of the electrons in a particular direction, creating a usable electrical current.
The Importance of Circuitry
In order to harness the energy input received by the photovoltaic cell, circuitry is essential. The electric current generated by the cell needs to be directed and regulated in order to power electrical devices or be stored for later use. Circuitry within the cell ensures that the electricity is efficiently utilized and distributed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a photovoltaic cell receives energy input primarily through sunlight, which excites the electrons in the semiconductor material and creates an electric current. The cell’s structure and circuitry play essential roles in capturing and utilizing this energy input. As advancements in technology continue, the efficiency and effectiveness of photovoltaic cells will only improve, making solar energy an increasingly viable and sustainable power source for the future.



