How a Photovoltaic Cell Receives Energy Input
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. The process by which a photovoltaic cell receives energy input primarily involves the interaction of light with semiconductor materials to produce an electric current.

1. Absorption of Sunlight
When sunlight strikes the surface of a photovoltaic cell, the semiconductor materials within the cell absorb the photons (particles of light) and convert their energy into electrons.
2. Creation of Electron Hole Pairs
As the photons are absorbed, they create electron-hole pairs within the semiconductor material. Electrons are released from their atomic bonds, leaving behind positively charged holes.
3. Generation of Electric Field
The separated electrons and holes create an electric field within the cell, as electrons are pushed towards one side of the cell and holes towards the other, creating a potential difference.
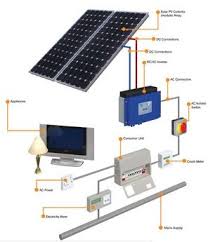
4. Collection of Electrons
The electric field within the cell causes the electrons to flow in one direction, creating a current that can be harnessed for electricity generation.
5. Conversion to Usable Electricity
The flowing electrons can be captured by metal contacts on the cell, which can then be connected to an external load to power electrical devices.
The Future of Photovoltaic Technology
The ability of photovoltaic cells to receive energy input from sunlight and convert it into electricity has made them a key player in the transition towards renewable energy sources. With advancements in technology, the efficiency and affordability of photovoltaic cells continue to improve, making solar power an increasingly viable option for meeting the world’s energy needs.
As the demand for clean energy grows, research and development in photovoltaic technology are focused on enhancing the performance of solar cells and reducing their production costs. This progress will undoubtedly contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy landscape in the future.

