How a Photovoltaic Cell Receives Energy Input
The Basics of Photovoltaic Cells
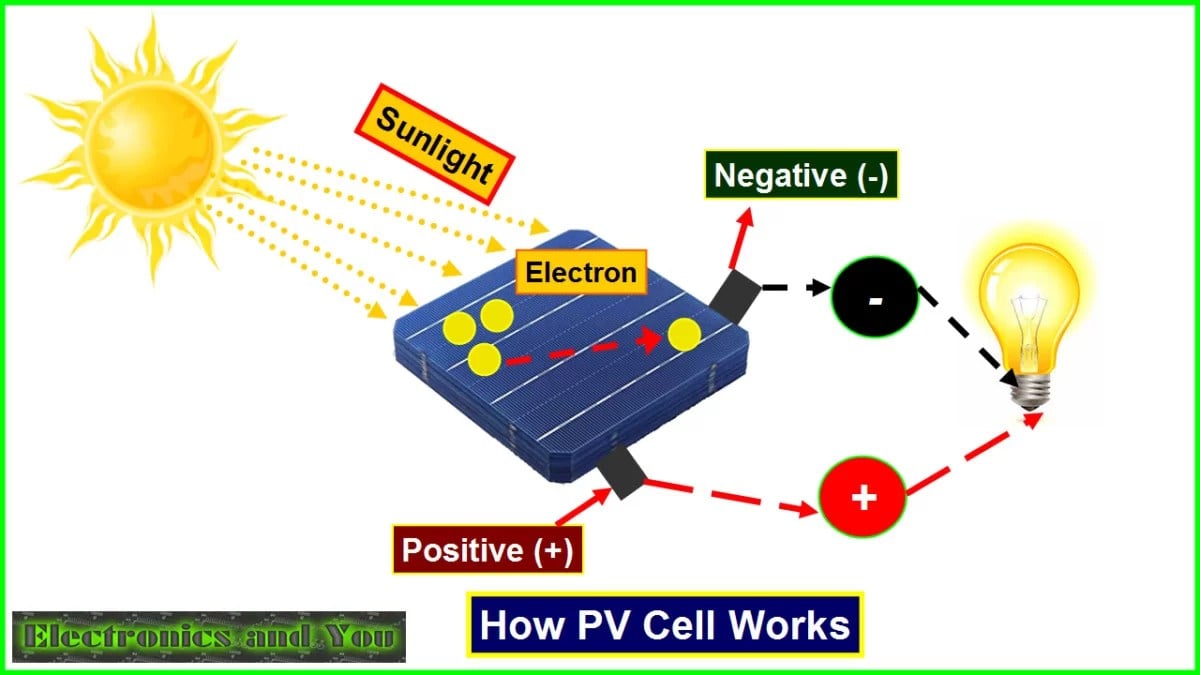
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light energy into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect. This process involves the absorption of photons from sunlight, which causes electrons to be released from the atoms in the cell, creating an electric current.
Direct Energy Input
The primary source of energy input for a photovoltaic cell is sunlight. When sunlight strikes the surface of the cell, it is absorbed by the semiconductor material, commonly silicon, and the energy from the photons is used to knock loose electrons from the atoms in the material, creating an electric current.
Secondary Energy Input
In addition to direct sunlight, photovoltaic cells can also receive energy input from ambient light. This means that even on cloudy days or in shaded areas, the cells can still generate electricity, although at a reduced efficiency compared to direct sunlight.
The Role of the Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is the process by which the energy from light is converted into electrical energy. It involves the generation of an electric current when photons strike the surface of the cell and release electrons, which then flow through the circuit to produce usable electricity.

Conclusion
In conclusion, a photovoltaic cell primarily receives energy input from sunlight, which is then converted into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect. This process allows for the generation of clean and renewable electricity from the sun’s abundant energy.



