How does a Photovoltaic Cell Work
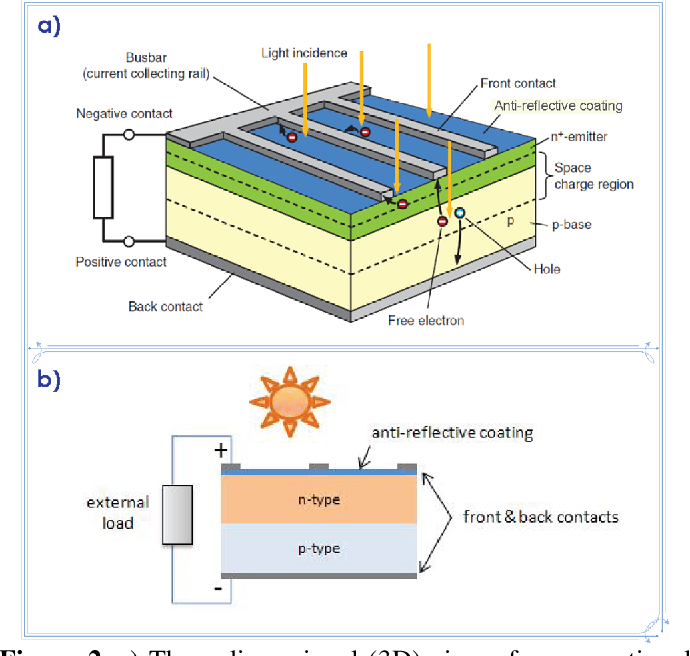
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are the key components of solar panels. These cells are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. But how exactly do photovoltaic cells work?
The Basics of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are made from semiconductor materials, like silicon. When sunlight hits the cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor, creating an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect.The Structure of a Photovoltaic Cell
A typical photovoltaic cell consists of multiple layers. The top layer is made from a material that allows sunlight to pass through and reach the semiconductor layer. The semiconductor layer is where the photovoltaic effect takes place, creating an electric field within the cell. The bottom layer is made from a material that collects the electrons and allows them to flow out of the cell as electricity.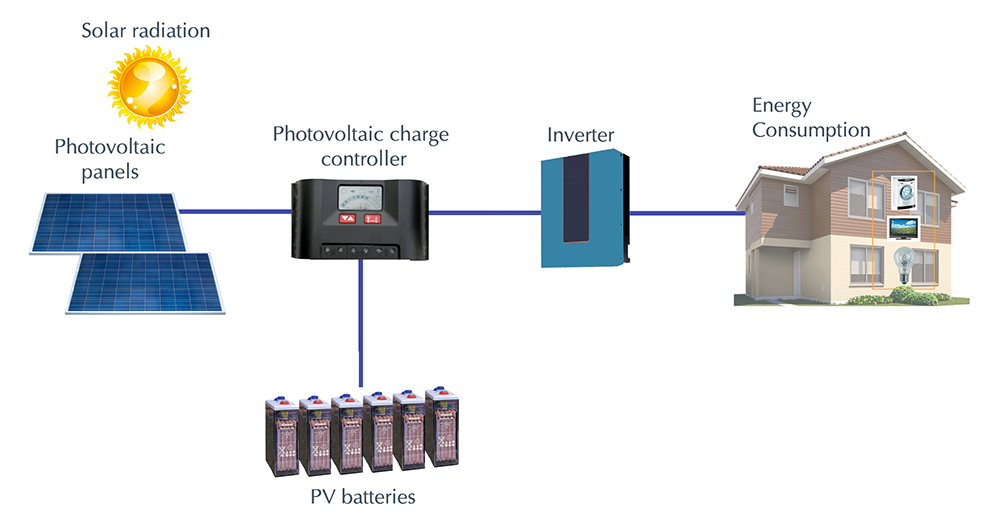
The Role of Sunlight
Sunlight is essential for the operation of photovoltaic cells. The photons in sunlight have enough energy to excite the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This is why photovoltaic cells are most effective when they are exposed to direct sunlight.The Generation of Electricity
Once the electrons are excited by sunlight and create an electric current, this current is then captured and channeled through the wiring of the solar panel. It can then be used to power electrical devices or stored in a battery for later use.The Future of Photovoltaic Cells
As technology advances, photovoltaic cells continue to become more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. They are also becoming more affordable, making solar power an increasingly popular choice for clean and renewable energy.In conclusion, photovoltaic cells work by harnessing the energy from sunlight and converting it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. As the demand for clean energy grows, photovoltaic cells will play a crucial role in meeting our energy needs in the future.

