A Solar Panel: Harnessing the Power of Photovoltaic Cells

The Power of Solar Panels
As the world continues to shift towards sustainable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a frontrunner in the race to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. At the heart of this renewable energy solution is the solar panel, which harnesses the power of photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity.
The Function of a Solar Panel
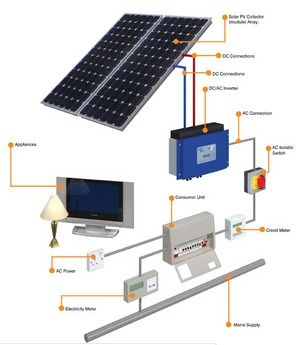
A solar panel combines multiple photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, which are made from materials such as silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it creates an electric field across the layers, causing electricity to flow. This direct current (DC) is then converted into alternating current (AC) by an inverter, making it compatible with the electrical grid.
Types of Photovoltaic Cells
There are three main types of photovoltaic cells: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film. Monocrystalline cells are made from a single crystal structure, providing higher efficiency and a sleek black appearance. Polycrystalline cells, on the other hand, are made from multiple silicon fragments, making them less efficient but more cost-effective. Thin-film cells use layers of materials like cadmium telluride or amorphous silicon, offering flexibility and lighter weight.
The Benefits of Solar Panels
Investing in solar panels offers numerous benefits, including reduced energy bills, lower carbon footprint, and increased independence from traditional energy sources. Furthermore, solar panels require minimal maintenance and have a lifespan of 25 years or more, making them a long-term investment in sustainable energy.
Conclusion
As the demand for clean energy continues to grow, the role of solar panels in the transition towards renewable power cannot be overstated. By harnessing the power of photovoltaic cells, solar panels are paving the way for a brighter, more sustainable future.

