The process of how a photovoltaic cell works
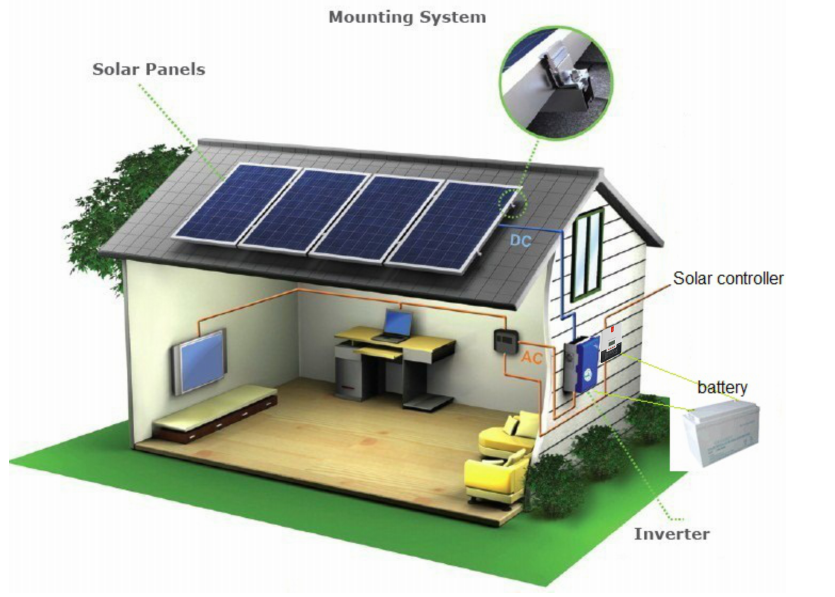
What is a photovoltaic cell?
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are made of materials such as silicon, which is a semiconductor that can absorb sunlight and release electrons. When multiple photovoltaic cells are connected together, they form a solar panel, which can generate higher amounts of electricity.How do photovoltaic cells work?
When sunlight hits the surface of a photovoltaic cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material. This causes the electrons to break free from their atoms and flow through the material, creating an electrical current. This flow of electrons is then captured by metal contacts on the top and bottom of the cell, allowing it to be harnessed as electricity.Internal structure of a photovoltaic cell
Inside a photovoltaic cell, there are multiple layers of semiconductor materials, each with different electrical properties. The most commonly used material is silicon, which has a p-n junction that separates the positive and negative charges created by the sunlight. This creates an electric field within the cell, which helps to drive the flow of electrons and produce electricity.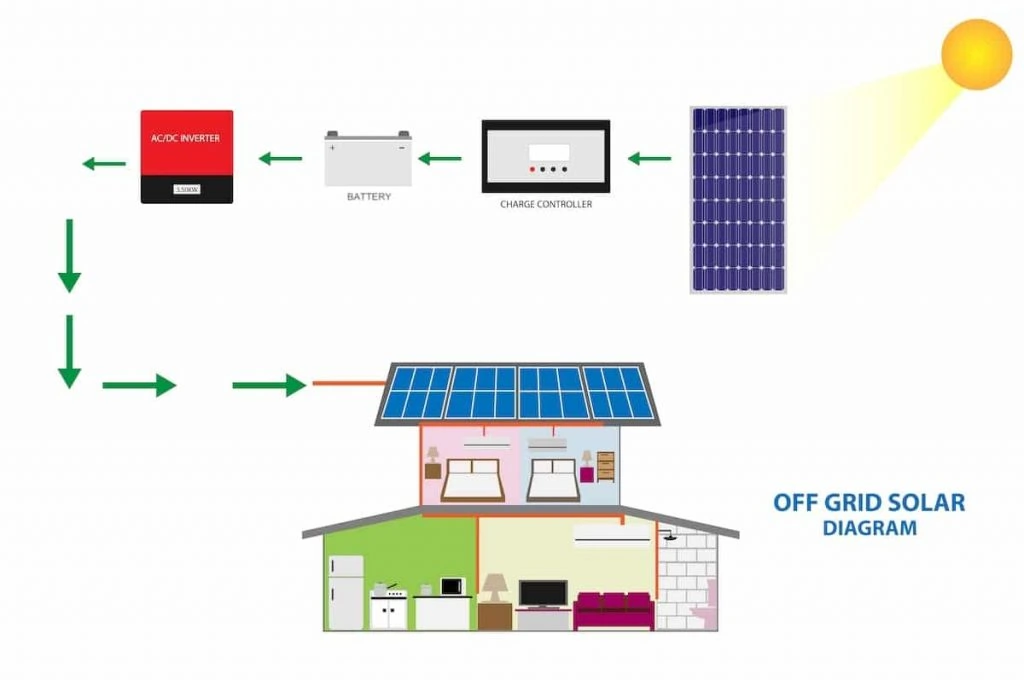
Conversion of sunlight to electricity
The photons in sunlight carry energy, and when they strike the surface of a photovoltaic cell, they transfer this energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material. This causes the electrons to gain enough energy to move and generate an electric current. The more sunlight that hits the cell, the more electrons are excited, and the more electricity is produced.Direct current output
The electricity generated by a photovoltaic cell is in the form of direct current (DC), which is the same type of electricity produced by batteries. This DC electricity can be used to power a variety of devices, ranging from small electronics to larger appliances, or it can be converted into alternating current (AC) using an inverter to be used in homes or businesses.Applications of photovoltaic cells
Photovoltaic cells are commonly used in solar panels, which can be installed on rooftops, in solar farms, or as standalone systems. They are a clean and renewable source of energy that can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities. With advancements in technology, the efficiency and affordability of photovoltaic cells continue to improve, making them an increasingly popular choice for sustainable energy production.In conclusion, photovoltaic cells work by converting sunlight into electricity through the movement of electrons in semiconductor materials. This process allows for the generation of clean and renewable energy that can be used in various applications. As the demand for sustainable energy sources continues to grow, photovoltaic cells are poised to play a crucial role in meeting these needs.

