Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are the building blocks of solar panels. They are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity, making them a crucial component in the production of clean, renewable energy. In this article, we will explore how photovoltaic cells are constructed and how they work to harness the power of the sun.
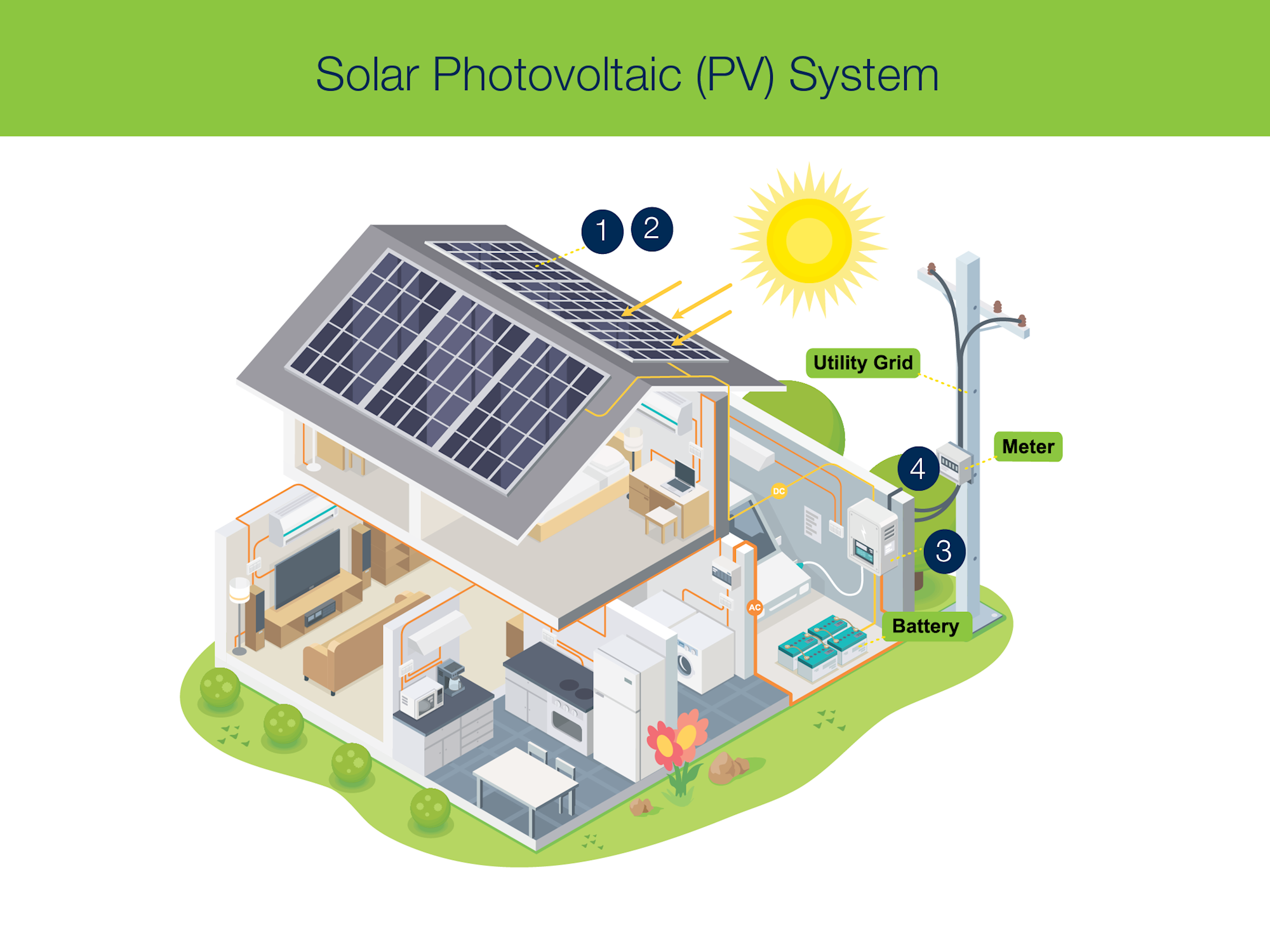
What are photovoltaic cells?
Photovoltaic cells are made from semiconductor materials such as silicon, which have the ability to convert sunlight into electricity. When photons from the sun’s rays strike the surface of the solar cell, they knock electrons loose from the atoms in the semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect, and it is the fundamental principle behind how solar cells generate electricity.Construction of photovoltaic cells
There are several layers that make up a typical photovoltaic cell. The main components include a top metal grid, an anti-reflective coating, a semiconductor layer, and a bottom metal contact. The semiconductor layer is usually made of silicon, which is a versatile material that can be doped with different elements to create either a positive (p-type) or negative (n-type) charge.Semiconductor layer
The semiconductor layer is where the magic happens. It is where the photons from sunlight are absorbed, and where the photovoltaic effect takes place. The p-type and n-type layers create an electric field at the junction between them, which causes the free electrons and holes created by the photons to separate and create an electric current.
Anti-reflective coating
The anti-reflective coating is applied to the top surface of the solar cell to reduce the amount of sunlight that is reflected away. This allows more photons to be absorbed by the semiconductor layer, increasing the overall efficiency of the solar cell.Metal grid and contacts
The top metal grid is responsible for collecting the electrons that are generated by the photovoltaic effect and transporting them to the electrical circuit. The bottom metal contact serves as the negative terminal of the solar cell, completing the electrical circuit and allowing the current to flow.How photovoltaic cells work
Once the photovoltaic cells are constructed and assembled into a solar panel, they can be used to generate electricity. When sunlight strikes the surface of the solar panel, the photovoltaic cells convert the energy from the sun into electricity, which can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other applications.In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are a crucial part of the solar energy revolution. By understanding how they are constructed and how they work, we can appreciate the ingenuity and technology behind solar panels, and the potential they have to provide clean, sustainable energy for the future.

