How Do Organic Photovoltaics Work?
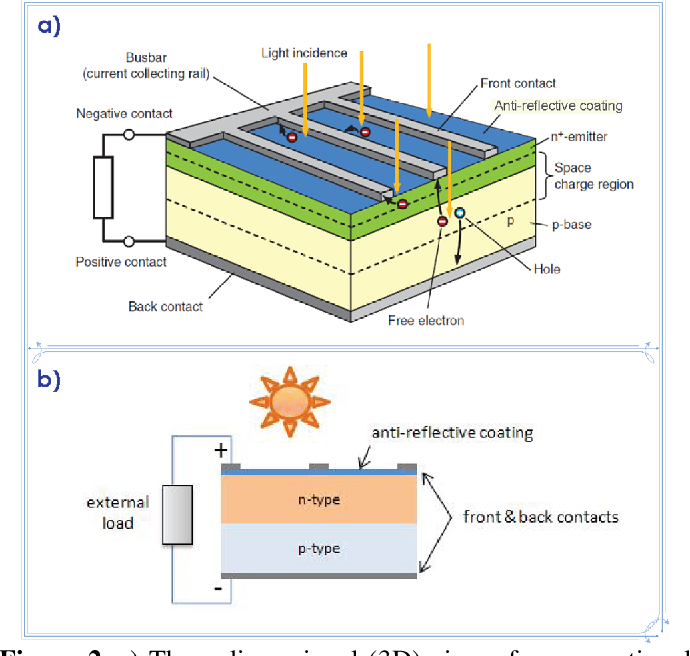
Organic photics, or OPVs, are a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based solar panels. These photovoltaics work by converting sunlight into electricity using organic molecules, such as polymers or small molecules, to harness the power of the sun. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of organic photovoltaics and how they compare to traditional solar cells.
The Basics of Organic Photovoltaics
Organic photovoltaics are composed of thin layers of organic materials that are deposited onto a substrate, such as glass or plastic. When light hits the organic layer, it creates electron-hole pairs, which generate an electric current. The key to the efficiency of organic photovoltaics lies in the properties of the organic materials used, such as their ability to absorb light and transport charge.
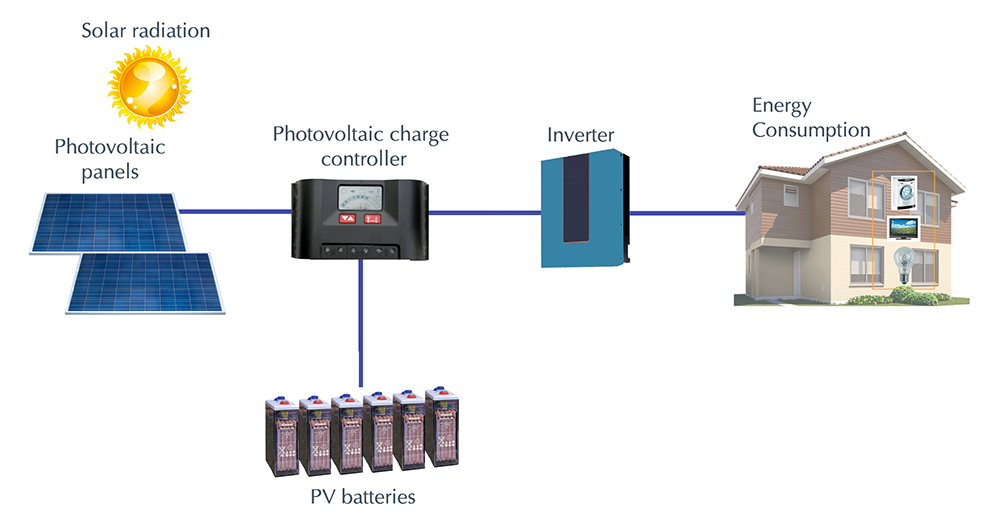
How Do Organic Photovoltaics Generate Electricity?
Organic photovoltaics generate electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. When photons from sunlight strike the organic layer, they are absorbed by the organic materials, causing them to release electrons. These electrons then flow through the material, creating an electric current. This process is similar to how traditional solar cells work, but organic photovoltaics have the advantage of being lightweight, flexible, and potentially lower cost to produce.The Advantages of Organic Photovoltaics
Organic photovoltaics offer several advantages over traditional silicon-based solar panels. These include flexibility, transparency, and the potential for low-cost manufacturing. Because organic photovoltaics can be made in thin, flexible layers, they can be integrated into a wide range of products, such as clothing, windows, and even mobile devices. Additionally, their transparency makes them suitable for building-integrated photovoltaics, where they can be used as windows or skylights.
The Challenges of Organic Photovoltaics
While organic photovoltaics have many advantages, they also face several challenges. One of the main challenges is their lower efficiency compared to traditional solar cells. Organic photovoltaics currently have a lower power conversion efficiency, meaning they are less efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. Additionally, the long-term stability and durability of organic photovoltaics are still being researched and developed.
The Future of Organic Photovoltaics
Despite the challenges, organic photovoltaics show great promise for the future of solar energy. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving the efficiency, stability, and scalability of organic photovoltaics. With continued advancements in organic materials and manufacturing processes, organic photovoltaics have the potential to become a widespread and cost-effective source of renewable energy.
In conclusion, organic photovoltaics work by utilizing organic materials to convert sunlight into electricity. While they offer several advantages over traditional solar panels, they also face challenges such as lower efficiency and long-term stability. However, with ongoing research and development, organic photovoltaics hold great potential for the future of solar energy.

