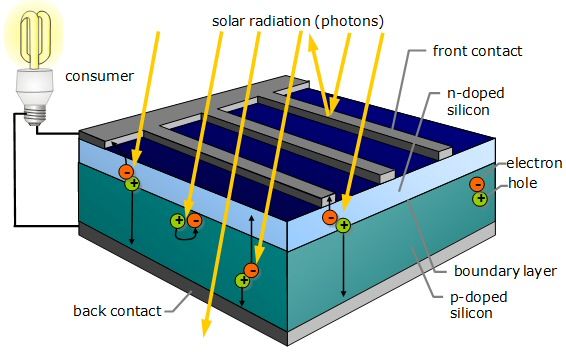
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are at the of solar panels and are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. This amazing process is made possible by the unique properties of certain materials and the principles of physics. In this article, we will explore how photovoltaic cells in solar panels work.
What are photovoltaic cells?
Photovoltaic cells are made fromiconducting materials, such as silicon, which have the ability to convert sunlight directly into electricity. When light strikes the surface of the solar cell, it is absorbed by the semiconductor material, causing electrons to be released. These electrons then flow through the material, creating an electrical current.How do photovoltaic cells work?
The process by which photovoltaic cells work can be broken down into several steps. First, photons from sunlight strike the surface of the solar cell, transferring their energy to the semiconductor material. This energy causes some of the electrons in the material to break free from their atoms, creating electron-hole pairs.The semiconductor material
The semiconductor material used in photovoltaic cells is typically doped with other elements to create a built-in electric field. This field causes the free electrons and holes to move in opposite directions within the cell, creating a flow of current.