How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work Differently Than Parabolic Solar Collection?
When it comes to harnessing the power of the sun, there are two main technologies that are commonly used: photovoltaic cells and parabolic solar collectors. While both of these systems are designed to capture solar energy, they work in fundamentally different ways. In this article, we will explore how photovoltaic cells and parabolic solar collection differ in operation and effectiveness.
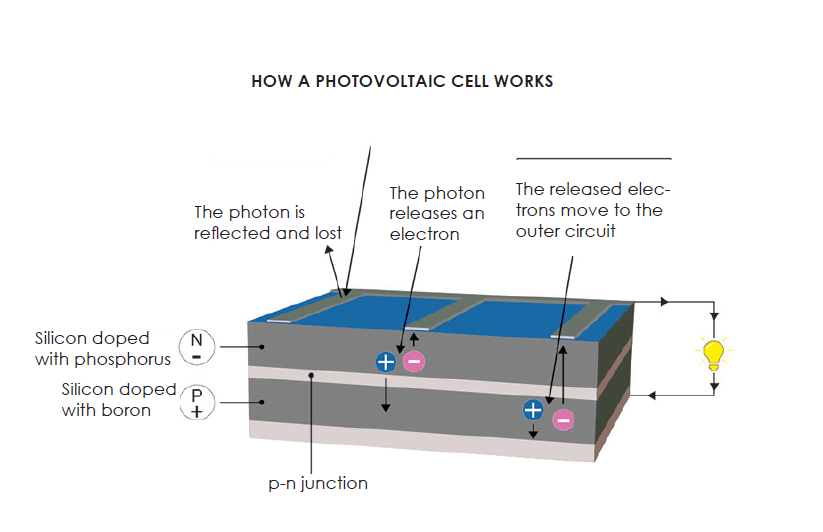
Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are made from layers of semiconducting materials such as silicon. When sunlight strikes the cells, it excites the electrons in the material, creating an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect, and it is the basis for how solar panels generate electricity. The resulting direct current (DC) electricity can be converted into alternating current (AC) through the use of an inverter, making it suitable for use in homes and businesses.
Parabolic Solar Collection
Parabolic solar collectors, on the other hand, are designed to concentrate sunlight onto a single focal point using reflective surfaces. This concentrated sunlight is used to heat a fluid, such as oil or water, which then produces steam to drive a turbine and generate electricity. This method is often used in large-scale solar power plants, where the concentrated sunlight can generate high temperatures and produce large amounts of electricity.
Differences in Efficiency
One of the key differences between photovoltaic cells and parabolic solar collection is their efficiency. Photovoltaic cells are able to directly convert sunlight into electricity with relatively high efficiency, typically around 15-20% for standard silicon-based cells. Parabolic solar collectors, on the other hand, have a lower efficiency in converting sunlight to electricity, but they are more effective in capturing and concentrating sunlight to produce high temperatures for power generation.
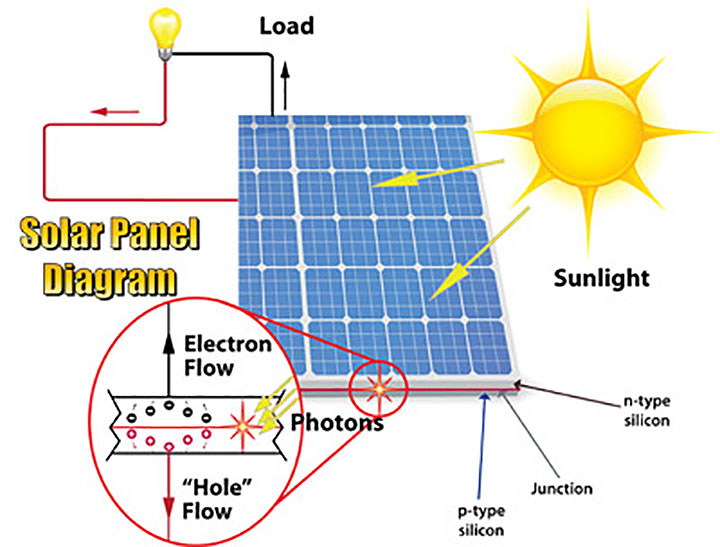
Environmental Considerations
Another important factor to consider when comparing these two technologies is their environmental impact. Photovoltaic cells have a minimal environmental footprint, as they produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants. Parabolic solar collection, while effective in generating electricity, typically requires a larger land area and may have a higher impact on local ecosystems due to the concentration of heat and the use of large-scale infrastructure.
Cost and Application
Cost and application also play a crucial role in determining which technology is best suited for a particular use case. Photovoltaic cells are more commonly used in residential and commercial applications due to their modular design and ease of installation. Parabolic solar collection is better suited for utility-scale power generation, where the high-temperature steam produced can be used to drive large turbines for electricity production.
Conclusion
While both photovoltaic cells and parabolic solar collection are effective in harnessing solar energy, they operate in different ways and have distinct advantages and limitations. Understanding the differences between these technologies can help in choosing the most suitable option for a specific solar energy application.

