How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work: A Simple Explanation

What are Photovoltaic Cells?
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are electronic devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which can absorb photons from the sun and convert them into electrons.How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work?
1. Absorption of Sunlight
When sunlight hits a photovoltaic cell, the semiconductor material absorbs the photons from the sun. The energy from the photons causes the electrons in the material to become excited and move, creating an electric current.2. Generation of Electricity
As the excited electrons move, they create a flow of electric current. This flow of current is then captured and channeled through electrical contacts on the solar cell, creating usable electricity.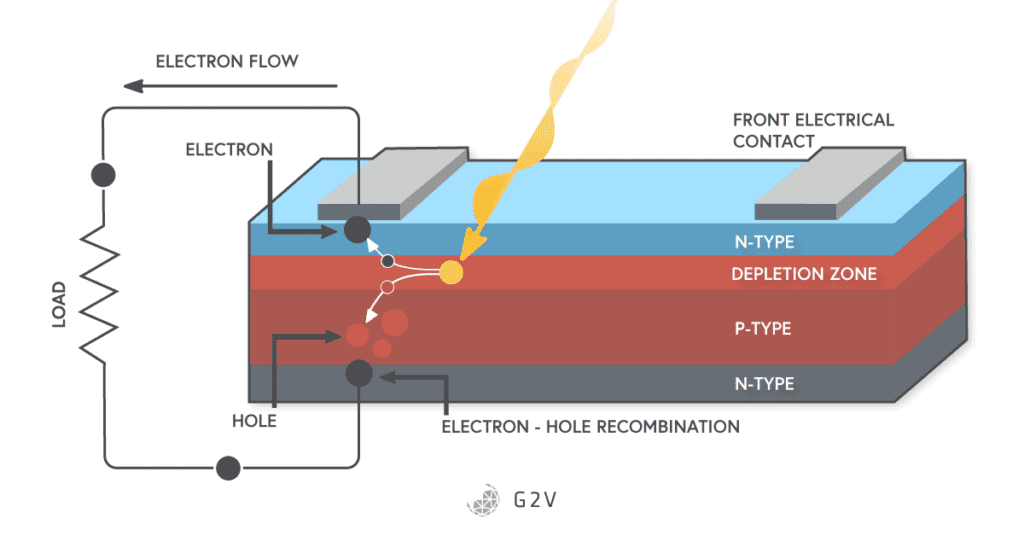
Benefits of Photovoltaic Cells
1. Renewable Energy Source
Since photovoltaic cells rely on sunlight, they provide a renewable source of energy that is abundant and inexhaustible. This makes them an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.2. Cost-Effective Energy Production
Once installed, photovoltaic cells require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a cost-effective solution for producing electricity.3. Reducing Carbon Emissions
By using photovoltaic cells to generate electricity, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions, contributing to a healthier planet.In conclusion, photovoltaic cells work by harnessing the energy of sunlight and converting it into electricity through the movement of electrons in semiconductor materials. This process provides numerous benefits, including renewable energy production, cost-effectiveness, and reduced environmental impact. As technology continues to advance, photovoltaic cells are becoming an increasingly important and viable solution for meeting our energy needs.

