How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work: A Comprehensive Guide
What are Photovoltaic Cells?
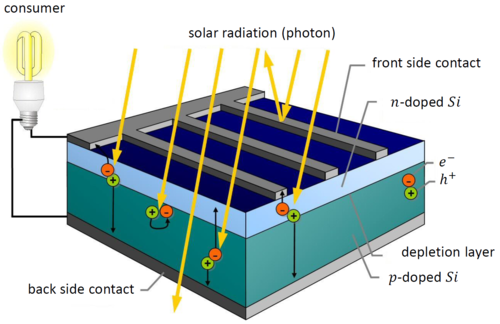
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that generate an electric current when exposed to light.
How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work?
When sunlight hits a photovoltaic cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to flow and create an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect.
Semiconductor Material
The most common semiconductor material used in photovoltaic cells is silicon. Silicon is doped with other elements to create a positive and negative charge. When sunlight hits the cell, it knocks loose electrons, creating an electric current.

Electric Field
Photovoltaic cells have an electric field across the layers of the cell, which helps to separate the negatively and positively charged electrons. This creates a flow of electric current within the cell.
Electricity Generation
As sunlight continues to hit the cell, it generates a continuous flow of electricity. This electricity can be used to power various devices, from small calculators to large-scale power plants.
Applications of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are used in a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial solar panels for electricity generation. They are also used in portable solar chargers and other small-scale devices that require electricity.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic cells are a key technology in the transition to renewable energy. Understanding how they work can help us harness the power of sunlight to create a sustainable energy future.

