How Do Semiconductor Photovoltaics Work?
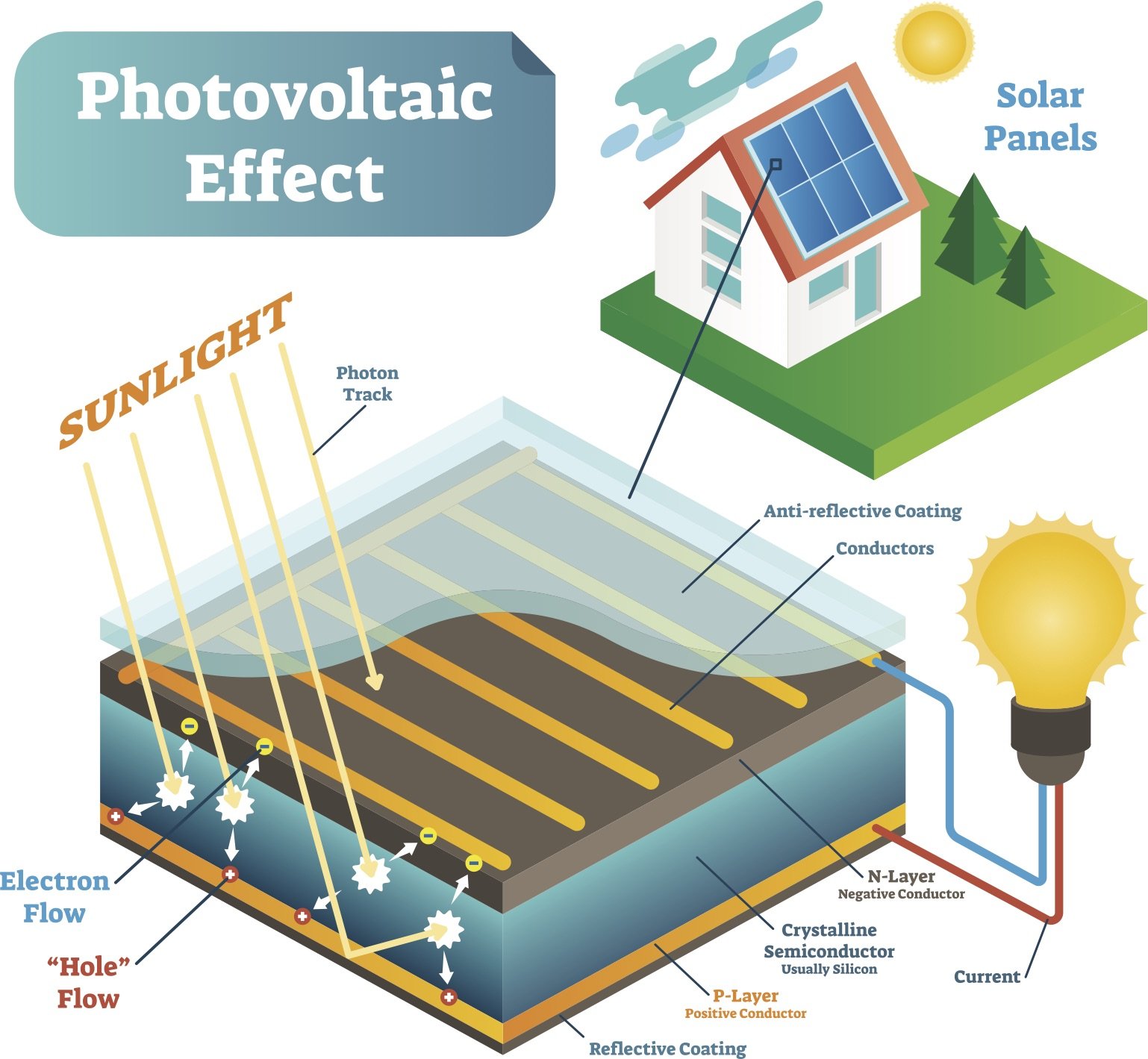
Semiconductor photovoltaic devices, commonly known as solar cells, are a type of technology that converts light energy into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. These devices are widely used in solar panels to generate electricity for various applications. But how exactly do semiconductor photovoltaics work? Let’s take a closer look at the underlying principles and mechanisms.
Basic Structure of Semiconductor Photovoltaics
Semiconductor Material
The key component of a semiconductor photovoltaic device is the semiconductor material, typically made of silicon. Silicon is a popular choice due to its abundance and favorable electronic properties. Other semiconductor materials such as cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide are also used in specific types of solar cells.
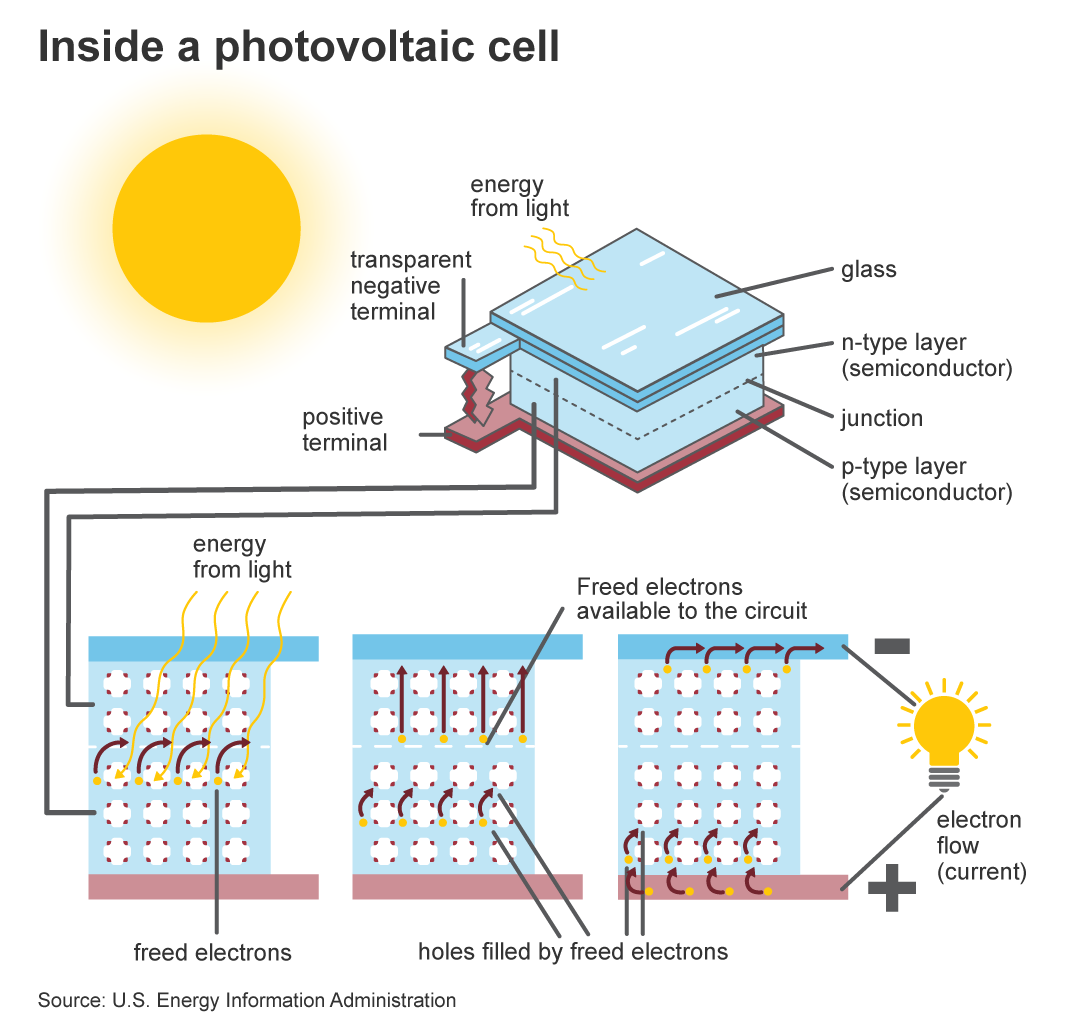
P-N Junction
The semiconductor material is doped to create a p-n junction, where one side becomes positively charged (p-type) and the other side becomes negatively charged (n-type). This creates an electric field across the junction, which plays a crucial role in the functioning of the solar cell.
Photovoltaic Effect
Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs
When light, composed of photons, strikes the semiconductor material, it excites electrons, causing them to break free from their atomic bonds and create electron-hole pairs. This process is known as the generation of electron-hole pairs, and it is the initial step in converting light energy into electrical energy.
Separation of Charge Carriers
The electric field at the p-n junction causes the positively charged holes to move towards the n-type side and the negatively charged electrons to move towards the p-type side. This separation of charge carriers generates a potential difference, creating a flow of electrical current within the solar cell.
Collection of Electrical Energy
The flow of electrical current is then collected by metal contacts on the top and bottom of the semiconductor material, allowing the electrical energy to be harnessed for external use. This collected energy can be used to power electrical devices or stored in batteries for later use.
Conclusion
Semiconductor photovoltaics play a crucial role in the field of renewable energy by providing a clean and sustainable source of electricity. By understanding the basic principles of semiconductor photovoltaics, we can appreciate the technology behind solar panels and their contribution to the global effort in transitioning towards a greener and more sustainable energy landscape.

