How Do Solar Photovoltaic Cells Produce Electricity

Introduction to Solar Photovoltaic Cells
Solar photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light energy directly into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that can absorb photons and release electrons, generating an electric current.Working Principle of Solar Photovoltaic Cells
1. Absorption of Sunlight
When sunlight hits the solar cell, the semiconductor material absorbs the photons, causing the electrons to be released from their atoms.2. Generation of Electric Field
The release of electrons creates a flow of electric charge, resulting in the generation of an electric field across the cell.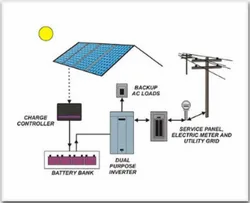
3. Collection of Electrons
The electric field forces the released electrons to move in a specific direction, where they are collected by metal contacts on the solar cell to form an electric current.Conversion of Electricity
1. Direct Current (DC)
The electricity generated by solar cells is in the form of direct current (DC), which is the same type of electricity produced by batteries.2. Inverters
To be used in homes and businesses, the DC electricity needs to be converted to alternating current (AC), which is done by using inverters.3. Utilization of Electricity
The converted AC electricity can then be used to power electrical devices, or it can be stored in batteries for later use.Advantages of Solar Photovoltaic Cells
– Renewable and Sustainable – Low Maintenance – Environmentally Friendly – Reduced Electricity Bills – Off-grid ApplicationsIn conclusion, solar photovoltaic cells work by converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. They offer numerous benefits and have the potential to play a significant role in meeting the world’s future energy needs.

