Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light energy into electrical energy through a process called the photovoltaic effect. This technology has become a popular renewable energy source as it allows for the generation of electricity from sunlight. But how exactly does a photovoltaic cell convert light to electricity? Let’s take a closer look at the process.
The Structure of a Photovoltaic Cell
A photovoltaic cell is typically made up of semiconductor materials such as silicon. These materials have special properties that allow them to convert sunlight into electricity. The cell is usually composed of several layers, each with a specific function in the conversion process.The Photovoltaic Effect
When light strikes the surface of the photovoltaic cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to move. This movement of electrons creates an imbalance of charge, leading to the generation of an electric current. This phenomenon is known as the photovoltaic effect and is the basis for how a solar cell produces electricity.Absorption of Photons
As sunlight hits the surface of the photovoltaic cell, the photons in the light are absorbed by the semiconductor material. This absorption of photons provides the energy needed to free electrons from their atomic bonds and allow them to move freely within the material.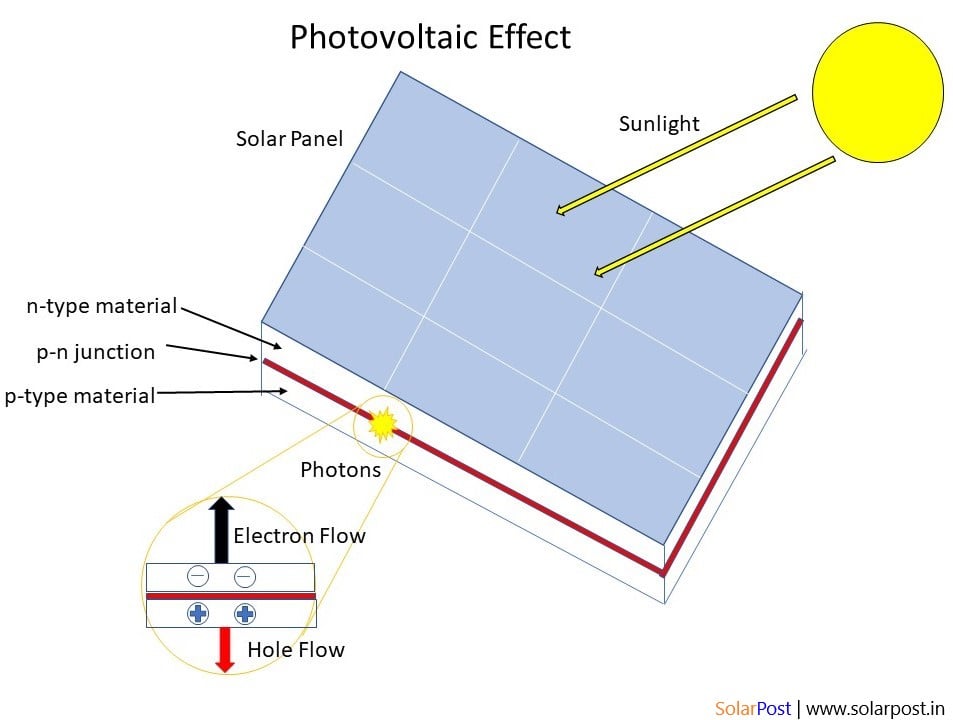
Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs
When the photons are absorbed, they transfer their energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material, allowing them to break free from their positions and leave behind positively charged “holes.” These liberated electrons and holes are then capable of conducting electricity, resulting in the generation of an electric current.Collection of Electrical Charge
Once the electrons and holes are generated, an electric field within the photovoltaic cell causes them to move in opposite directions. This electric field is created by the junction between the different layers of the cell. As a result, the electrons are collected by metal contacts on the cell, creating a flow of electrical current that can be harnessed for use.Conversion of Direct Current (DC)
The electric current produced by the photovoltaic cell is in the form of direct current (DC) electricity. To make this electricity usable for typical household appliances, it must be converted to alternating current (AC) through the use of an inverter. The converted electricity can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other electrical devices.In conclusion, a photovoltaic cell converts light to electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This process involves the absorption of photons, the generation of electron-hole pairs, the movement of electrical charge, and the collection of the resulting electric current. As the demand for renewable energy sources continues to grow, photovoltaic cells are expected to play a significant role in meeting these needs.

