Photovoltaic Cell: How It Converts Light to Electricity
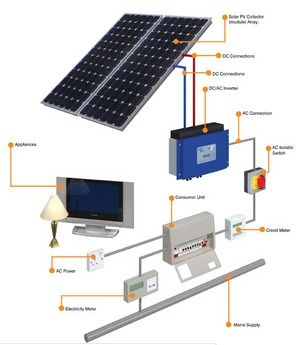
What is a Photovoltaic Cell?
A photovoltaic cell, also known as a solar cell, is a device that converts light energy into electrical energy using the photovoltaic effect. This effect occurs when photons from sunlight strike the cell, causing electrons to be knocked loose from atoms within the cell, generating an electric current.How Does a Photovoltaic Cell Work?
1. Absorption of Light
When light particles, or photons, strike the surface of the photovoltaic cell, they are absorbed by the semiconductor material within the cell.2. Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs
The absorbed photons give energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material, allowing them to break free from their atomic bonds and generate electron-hole pairs.
3. Separation of Charges
The electric field within the solar cell causes the separated electrons and holes to move in opposite directions, creating a potential difference and generating an electric current.4. Collection of Current
The electric current generated by the movement of the electrons and holes is collected by metal contacts on the top and bottom of the cell, which can then be used to power electrical devices.5. Conversion Efficiency
The efficiency of a photovoltaic cell in converting light to electricity depends on factors such as the material used, the design of the cell, and environmental conditions.Applications of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are commonly used in solar panels to generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They are also used in calculators, satellites, and other electronic devices.In conclusion, the photovoltaic cell is a remarkable piece of technology that plays a crucial role in harnessing solar energy and converting it into electricity. By understanding how a photovoltaic cell converts light to electricity, we can appreciate its significance in sustainable energy generation and its potential to reduce our reliance on non-renewable energy sources.

