How Does a Photovoltaic Cell Convert Sunlight to Electricity
Introduction
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are made of semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a process that converts sunlight into electrical energy. In this article, we will explore the working principle of photovoltaic cells and how they harness the power of sunlight to generate electricity.

Working Principle
When sunlight, which is made up of photons, strikes a photovoltaic cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material. This creates a flow of electricity, known as direct current (DC), within the cell. The semiconductor material is usually made of silicon, and when it is combined with other materials, such as phosphorous and boron, it becomes negatively and positively charged, creating an electric field within the cell.
Energy Conversion
As the electrons move through the electric field, they are pushed in one direction, creating an imbalance of electrons at the junction between the two layers of the semiconductor. This causes a flow of electrons, which is then captured and used as electrical energy.
Electricity Generation
The electrical energy generated by the photovoltaic cell can be used to power appliances, lighting, and electronic devices, or stored in batteries for later use. In some cases, excess electricity can be fed back into the grid, allowing homeowners and businesses to generate income from their solar energy systems.
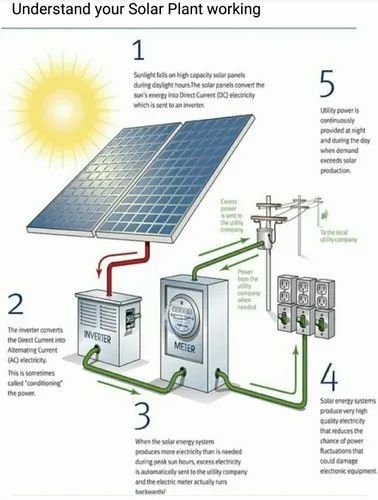
Efficiency and Applications
The efficiency of a photovoltaic cell is determined by its ability to convert sunlight into electricity. Advances in technology have led to the development of highly efficient solar cells, with some newer models reaching efficiencies of over 20%. Photovoltaic cells are used in a wide range of applications, from small-scale solar panels for residential use to large solar farms that generate electricity for entire communities.
Environmental Impact
One of the key benefits of photovoltaic cells is their minimal environmental impact. Unlike traditional energy sources, such as fossil fuels, solar energy does not produce harmful emissions or contribute to air or water pollution. As the world transitions towards renewable energy sources, the use of photovoltaic cells is expected to play a major role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to harness the power of sunlight and convert it into electricity. By understanding the working principle of photovoltaic cells and their applications, we can appreciate the potential of solar energy as a clean and renewable source of power for the future. As technology continues to advance, the efficiency and affordability of photovoltaic cells are expected to improve, further driving the global transition towards solar energy.



