How Does a Photovoltaic Cell Work

When it comes to harnessing the power of the sun, photovoltaic cells play a crucial role. Also known as solar cells these devices convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. In this article, we’ll explore the inner workings of a photovoltaic cell and how it generates clean, renewable energy.
Understanding the Photovoltaic Effect
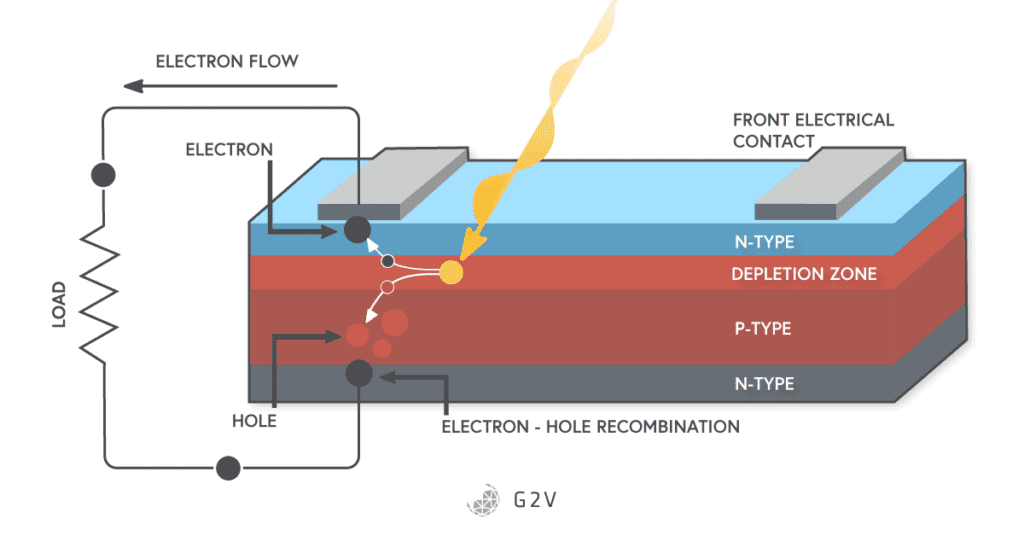
At the heart of a photovoltaic cell is the photovoltaic effect, which is the process of converting light into electricity. This process occurs when photons from sunlight interact with the semiconductor material in the cell, causing electrons to be released. These free electrons then create an electric current, which can be harnessed to power electrical devices.
Semiconductor Materials
Photovoltaic cells are typically made from semiconductor materials such as silicon. When light strikes the semiconductor, it excites the electrons in the material, allowing them to flow and generate an electric current. The design and composition of the semiconductor material are crucial in determining the efficiency and performance of the photovoltaic cell.
Formation of Electric Field
As the electrons are released in the semiconductor material, they create a buildup of negative charge, while the region from which the electrons have moved becomes positively charged. This separation of charge creates an electric field within the cell, which encourages the flow of electrons in a single direction, generating a steady current.
Construction of a Photovoltaic Cell
A typical photovoltaic cell consists of multiple layers of semiconductor materials, each performing a specific function in the conversion of sunlight into electricity. At the top layer, a transparent conductive material allows sunlight to pass through while collecting the generated electricity. Beneath this is the semiconductor layer where the photovoltaic effect takes place, followed by a metal layer that conducts the electric current out of the cell.
Collection of Electricity
Once the electric current is generated within the photovoltaic cell, it is collected and channeled through an external circuit for use. This circuit may include wires to carry the current and an inverter to convert the direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) for use in household appliances and electrical grids.
Applications of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are widely used in solar panels to generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They can also be integrated into building materials such as roof tiles and windows to provide a dual function of energy generation and architectural design.
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are a vital component in the generation of clean, renewable energy from sunlight. By understanding the photovoltaic effect and the construction of these cells, we can appreciate the technology behind solar energy and its potential to power a sustainable future.

