How does a Solar Photovoltaic System Work
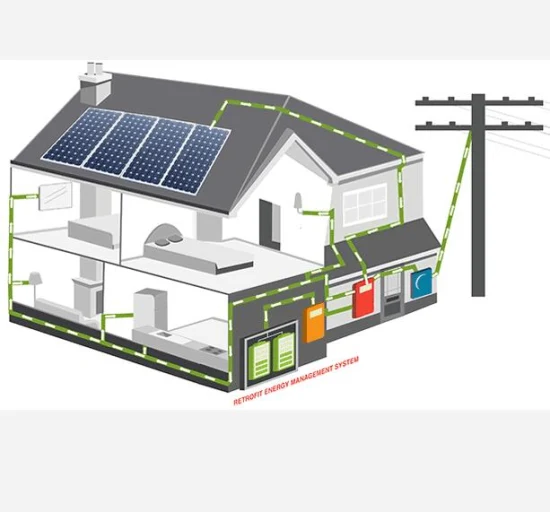
So, you’ve decided to go solar and are considering installing a solar photovoltaic system on your property. But how exactly does it work? Let’s break it down.
1. Photovoltaic Cells
The heart of a solar photovoltaic system is the photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, usually silicon, and when sunlight hits the cells, it excites the electrons, causing them to flow and create an electric current.
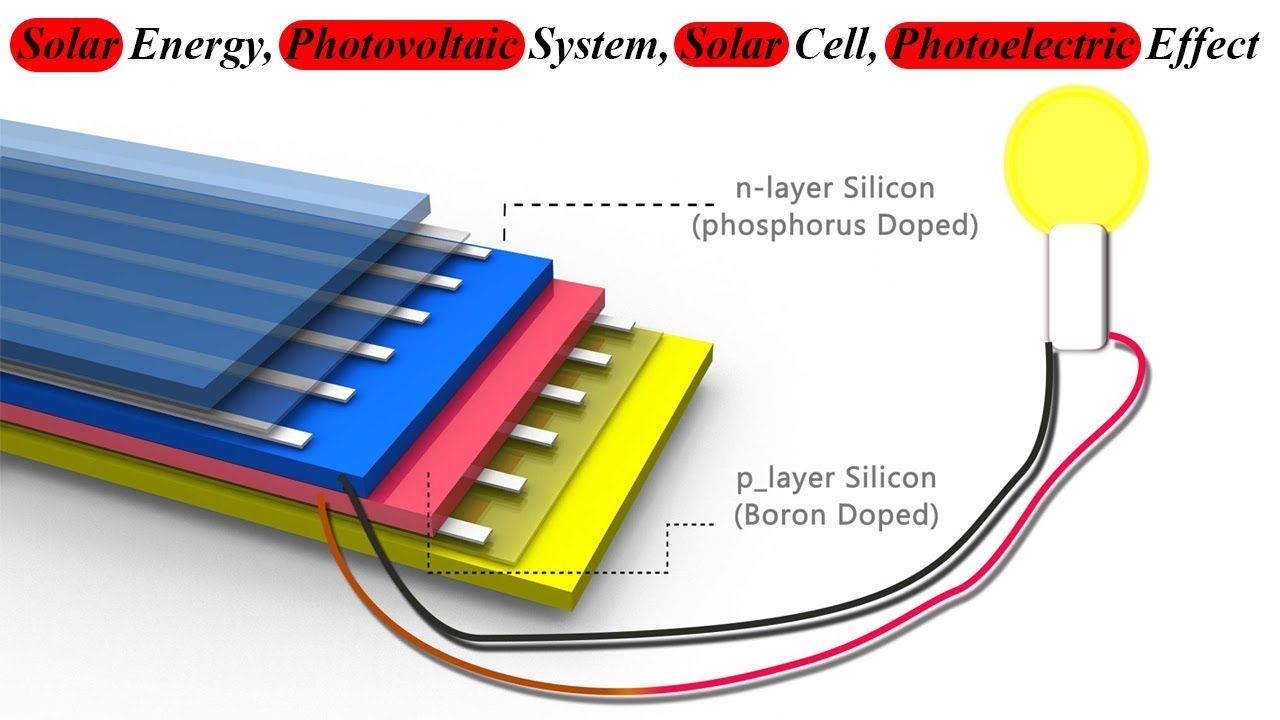
2. Solar Panels
Multiple PV cells are connected and encapsulated within solar panels, also known as modules. These panels are then installed on the roof or ground, where they can capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
3. Inverter
The electricity generated by the solar panels is in the form of direct current (DC), but most home appliances and the grid operate on alternating current (AC). This is where the inverter comes in. It converts the DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity that can be used in your home or fed back into the grid.
4. Net Metering
If your solar photovoltaic system is connected to the grid, you can take advantage of net metering. This means that any excess electricity produced by your system can be fed back into the grid, and you’ll receive credits for it on your electricity bill.
5. Monitoring and Maintenance
Once your solar photovoltaic system is up and running, it’s important to keep an eye on its performance and make sure it’s maintained properly. Many systems come with monitoring tools that allow you to track the electricity production and catch any issues early on.
In conclusion, a solar photovoltaic system works by harnessing sunlight through PV cells, converting it into usable electricity, and integrating it with your home or the grid. With advancements in technology and decreasing costs, solar power has become a viable and sustainable energy solution for many homeowners and businesses.

