Concentrated Solar Heating vs. Photovoltaic Cells: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to harnessing the power of the sun for renewable energy, two popular technologies come to mind: concentrated solar heating and photovoltaic cells. While both systems aim to capture sunlight and convert it into usable energy, they work in fundamentally different ways. In this article, we’ll explore how concentrated solar heating differs from photovoltaic cells.

How Concentrated Solar Heating Works
Concentrated solar heating, also known as concentrated solar power (CSP), utilizes mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight onto a small area. The concentrated sunlight is then used to heat a fluid such as water or molten salt, which in turn generates steam to drive a turbine and produce electricity. This method allows for the efficient collection of solar energy in areas with high levels of sunlight.
How Photovoltaic Cells Work
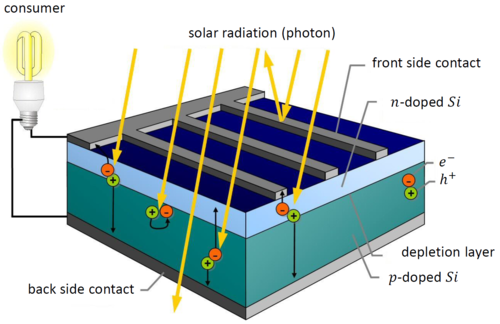
On the other hand, photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar panels, utilize semiconductor materials to directly convert sunlight into electricity. When photons of light strike the solar panel, they excite electrons in the semiconductor, generating a flow of electricity. This electricity can be used to power homes and businesses, or stored in batteries for later use.
The Key Differences
One of the primary differences between concentrated solar heating and photovoltaic cells lies in the way they capture and convert sunlight. Concentrated solar heating relies on the concentration of sunlight to generate heat, while photovoltaic cells directly convert sunlight into electricity. Additionally, concentrated solar heating is often used in large-scale utility applications, while photovoltaic cells are commonly used for distributed power generation on rooftops and in solar farms.
Efficiency and Reliability
Another important distinction is in the efficiency and reliability of the two technologies. Concentrated solar heating systems have the advantage of being able to store heat for use during periods of low sunlight, providing a more consistent power output. Photovoltaic cells, on the other hand, are highly efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, but their output can be affected by factors such as shading and temperature.
Environmental Impact
From an environmental standpoint, both concentrated solar heating and photovoltaic cells offer significant benefits in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. However, concentrated solar heating systems may require more land for installation, as they rely on large arrays of mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight. In contrast, photovoltaic cells can be installed on existing structures, making more efficient use of space.
Conclusion
In summary, concentrated solar heating and photovoltaic cells are two distinct technologies for harnessing solar energy. While concentrated solar heating relies on the concentration of sunlight to generate heat for electricity production, photovoltaic cells directly convert sunlight into electricity. Both technologies have their own advantages and limitations, and the choice between the two will depend on factors such as location, scale, and specific energy needs. By understanding the differences between these two solar technologies, we can better appreciate the diverse ways in which we can harness the power of the sun for a sustainable future.



