How Does Solar Photovoltaic Energy Work?
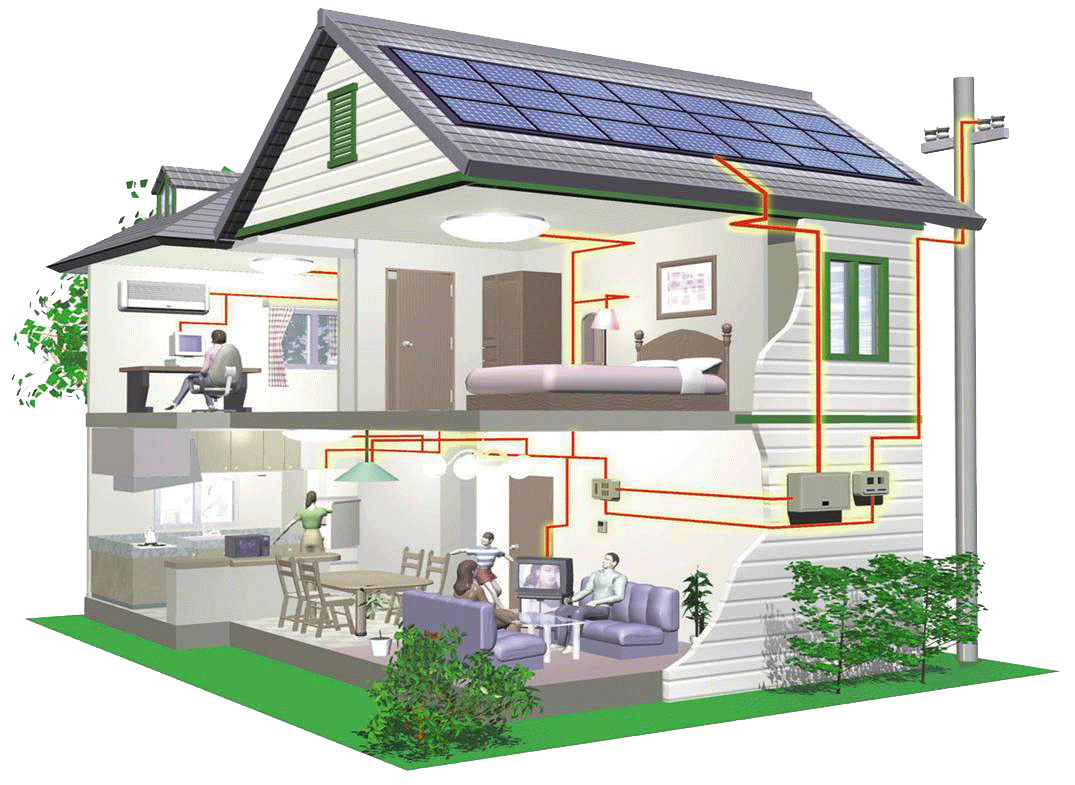
Solar photovoltaic energy, also known as solar PV, is a technology that converts sunlight into electricity. This renewable energy source has gained popularity in recent years due to its environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness. But how does solar photovoltaic energy work? Let’s break it down.
The Basics of Solar Photovoltaic Energy
Solar photovoltaic systems consist of solar panels, inverters, mounting hardware, and electrical wiring. The solar panels, also known as photovoltaic cells, are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon. When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photons in the sunlight knock electrons loose from the atoms within the semiconductor material, generating a flow of electricity.
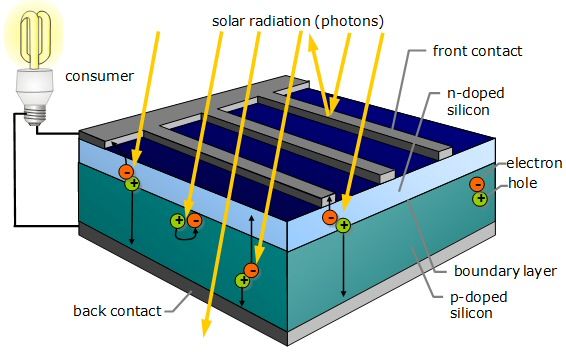
The Role of Inverters
Once the solar panels have generated electricity, it needs to be converted from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) in order to be used in homes and businesses. This is where inverters come into play. They are responsible for converting the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into the AC electricity that powers the electronic devices and appliances.
Net Metering and Grid Connection
In most solar photovoltaic systems, excess electricity generated during the day is sent back to the grid, and the homeowner receives credit for this excess power through a system called net metering. This means that on cloudy days or at night, when the solar panels are not generating enough electricity, the homeowner can draw power from the grid without incurring additional costs.
Environmental Benefits
One of the key advantages of solar photovoltaic energy is its environmental benefits. By generating electricity from sunlight, solar PV systems produce no greenhouse gas emissions, helping to combat climate change and reduce air pollution. Additionally, solar PV systems reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a more sustainable and cleaner energy future.
Cost-Effectiveness and ROI
Another attractive aspect of solar photovoltaic energy is its cost-effectiveness. While the initial investment in a solar PV system may seem significant, the long-term savings on electricity bills and potential government incentives and rebates make solar energy an economically viable option for many homeowners and businesses. Over time, the return on investment (ROI) for solar PV systems can be substantial.
Conclusion
In summary, solar photovoltaic energy works by capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity through the use of solar panels and inverters. This renewable energy source offers environmental benefits, cost-effectiveness, and the potential for long-term savings. As technology continues to advance, solar photovoltaic energy will play an increasingly important role in our transition to a sustainable energy future.

