How Much Energy Can a Solar Panel Produce?
Introduction
Solar panels are an increasingly popular way to harness renewable energy. As concerns about climate change and rising energy costs continue to grow, many homeowners and businesses are turning to solar power as a reliable, eco-friendly energy source. One of the most frequently asked questions about solar panels is how much energy they can produce. This article will delve into this question, offering detailed insights into solar panel efficiency, the factors that influence energy production, and how different use cases can benefit from solar technology.
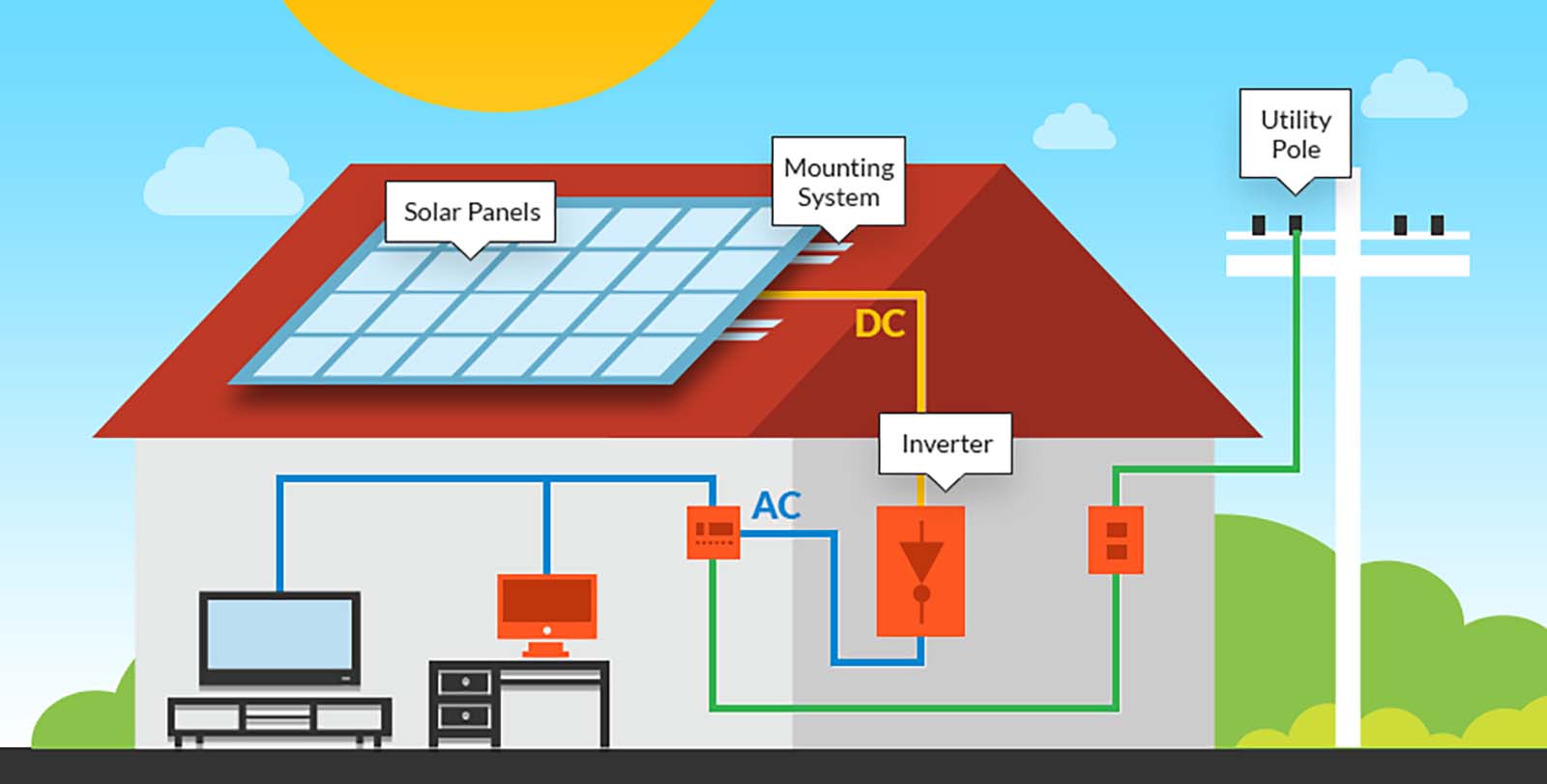
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. The amount of energy a panel can produce depends on several factors, including its efficiency, the location where it’s installed, and the amount of sunlight it receives. By understanding these factors, you can estimate how much energy your solar panels will produce and how they can meet your energy needs. Additionally, we will explore the role of solar batteries in storing excess energy, enhancing solar power systems for both residential and commercial use.
Understanding Solar Panel Output
The Basics of Solar Panel Energy Production
Solar panels are designed to convert sunlight into electrical energy using photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells absorb sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity, which is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity by an inverter. The energy output of a solar panel is measured in watts (W), and the capacity of a solar panel typically ranges from 250W to 400W per panel, depending on the model and the manufacturer.
The total energy production of a solar panel is directly related to several factors:
Panel Efficiency: The efficiency of a solar panel refers to its ability to convert sunlight into electricity. Higher-efficiency panels can produce more energy per square meter of surface area. Sunlight Availability: The amount of sunlight a panel receives depends on geographic location, time of year, and weather conditions. Areas with more sunlight will naturally produce more energy. Panel Orientation and Tilt: Panels should be installed at an angle and orientation that maximizes sunlight exposure. In the northern hemisphere, south-facing panels generally receive the most sunlight. Temperature: Solar panels are typically more efficient in cooler temperatures. Extremely hot conditions can reduce the efficiency of the panels.Average Energy Production of a Solar Panel
On average, a 300W solar panel will produce around 1.2 to 1.5 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per day, assuming it receives around 4 to 5 hours of direct sunlight each day. The actual energy output can vary depending on location, time of year, and environmental conditions.
For example, in sunny regions like California or Arizona, a 300W solar panel could produce between 1.5 to 1.8 kWh per day. In contrast, regions with less sunlight might see a daily output closer to 1 kWh per day.
Calculating Solar Panel Energy Output
To calculate how much energy your solar panels can produce, you’ll need to consider the following factors:
Panel Wattage: The wattage of each panel will give you a baseline for energy production. For example, a 300W panel generates 0.3 kWh of energy per hour of sunlight. Sunlight Hours: The average number of full sunlight hours your panels will receive per day, based on location. System Efficiency: The inverter and other system losses typically account for a reduction of around 10-20% in energy efficiency.Example Calculation:If you have 10 solar panels, each with a 300W capacity, and you receive 5 hours of sunlight per day, the energy produced would be:
[ 10 \, \text{panels} \times 300W \times 5 \, \text{hours} = 15,000W = 15 \, \text{kWh/day} ]
This would be the total energy your solar panel system could produce per day under optimal conditions.
Features of Solar Batteries and Their Role in Energy Storage
While solar panels generate energy during the day, they cannot produce electricity at night or during periods of low sunlight. This is where solar batteries come into play. A solar battery stores excess energy produced by the solar panels during the day, allowing homeowners and businesses to use that energy later, thus maximizing the benefits of solar power.
Key Features of Solar Batteries
Safety and Stability: Modern solar batteries are designed with built-in safety features to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and electrical failures. Batteries using LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) chemistry offer enhanced thermal stability and a low flammability risk, making them safer for residential and commercial use. Thermal Stability: Solar batteries are designed to operate efficiently across a wide temperature range. For example, some models can operate in temperatures ranging from -20°C to 60°C, making them adaptable to extreme weather conditions. Intelligent Interaction Capability: Many solar batteries come with multi-language touch screens that provide real-time monitoring of critical parameters such as power, voltage, and temperature. Additionally, many systems feature Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity for remote monitoring via an app.How Solar Batteries Enhance Energy Efficiency
Peak and Valley Tariff Strategy: Solar battery systems allow for time-based control of charging and discharging. By storing excess energy during peak sunlight hours and using it during periods of high electricity demand, users can save on energy bills, especially in regions with variable electricity tariffs. Emergency Backup Power: Solar batteries provide a reliable source of backup power in the event of an electrical outage, protecting essential appliances and systems like lights, refrigerators, and heating during emergencies.Applications of Solar Panels and Batteries
Residential Use Case: Home Energy Independence
For homeowners, solar panels combined with solar batteries provide an opportunity to reduce reliance on the grid, cut energy costs, and ensure access to power even during outages.
Reducing Energy Costs: By installing solar panels and batteries, homeowners can reduce their electricity bills by generating their own power and storing it for later use. Energy Independence: Solar systems can help homeowners become more self-sufficient, especially in areas with frequent power outages or high electricity costs.Enterprise Use Case: Commercial Applications
Businesses, particularly those with high energy consumption, can also benefit from solar panels and batteries. Commercial solar installations can help businesses reduce their energy costs and ensure continuity of operations in case of power failures.
Backup Power for Data Centers: For businesses relying on data centers, solar batteries can ensure uninterrupted power, protecting sensitive equipment and reducing the risk of costly downtimes. Optimized Solar Integration: Businesses can integrate solar power with their existing infrastructure to enhance efficiency, reduce operating costs, and meet sustainability goals.In conclusion, solar panels are a powerful tool for reducing energy bills and promoting sustainability. The amount of energy a solar panel can produce depends on factors like location, sunlight availability, panel efficiency, and system setup. When paired with solar batteries, these systems offer increased reliability, energy independence, and cost savings. By investing in solar energy today, you can contribute to a greener future while enjoying financial and environmental benefits.
Call to Action
Are you ready to harness the power of the sun? Contact us today to learn more about solar panel installations and how solar batteries can enhance your energy efficiency. Let’s work together to create a sustainable energy solution tailored to your needs!

