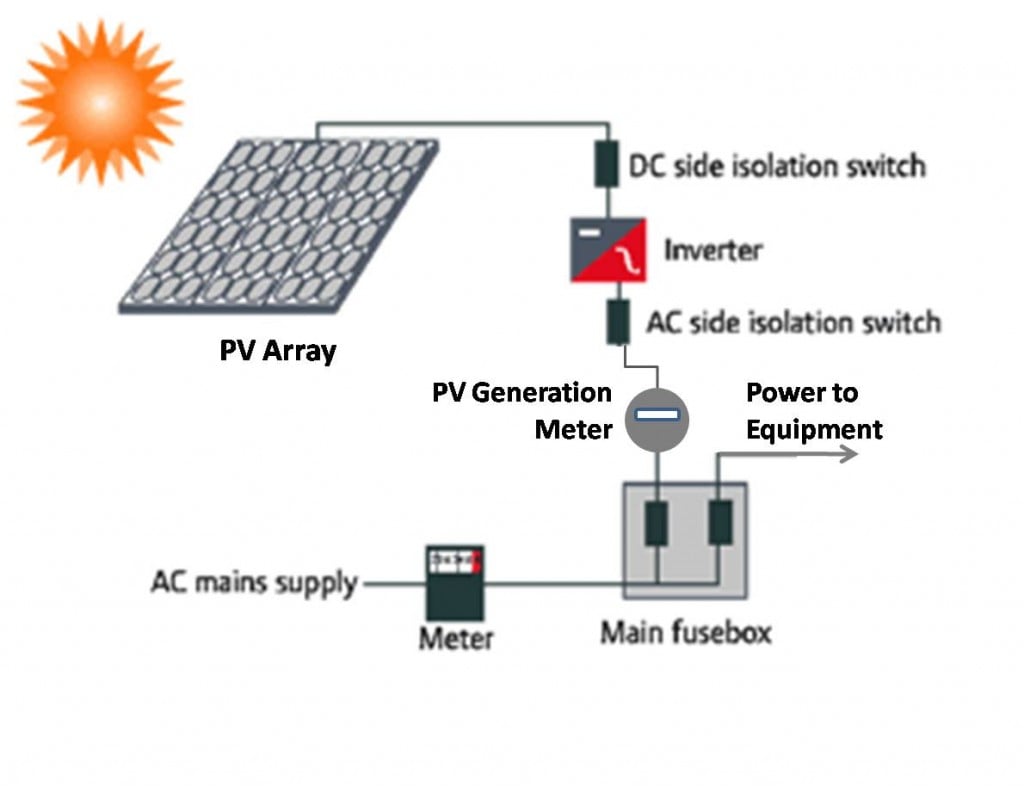
In today’s world, the demand for clean and renewable energy sources is at an all-time high. One of the most popular and widely-used sources of renewable energy is photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells. These innovative cells harness the power of the sun to produce electricity, and are a key component of solar panels used in both residential and commercial applications. But just how much energy can photovoltaic cells produce?

Understanding Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are made of semiconductor materials such as silicon, which have the unique ability to convert sunlight directly into electricity. When sunlight strikes the cells, it excites electrons in the semiconductor material, creating a flow of electricity. This process, known as the photoelectric effect, is the basis for how photovoltaic cells generate power.The Output of Photovoltaic Cells
The amount of energy that photovoltaic cells can produce varies depending on a number of factors, including the size and efficiency of the cells, the amount of sunlight available, and the angle at which the panels are installed. On average, a standard residential solar panel system with an area of around 12 square meters can produce between 3,600 to 5,400 kilowatt-hours of electricity per year. This is enough to power a typical household’s energy needs.Factors Affecting Energy Production
1. Size and Efficiency: Larger and more efficient photovoltaic cells will produce more electricity. 2. Sunlight Intensity: Areas that receive more sunlight will produce more energy. 3. Angle and Orientation: The angle and orientation of the solar panels can affect their energy production.