How Photovoltaic Cells Generate Electricity
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are made of materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, which is the phenomenon of generating an electric current when exposed to light. This article will explain the process of how photovoltaic cells generate electricity.
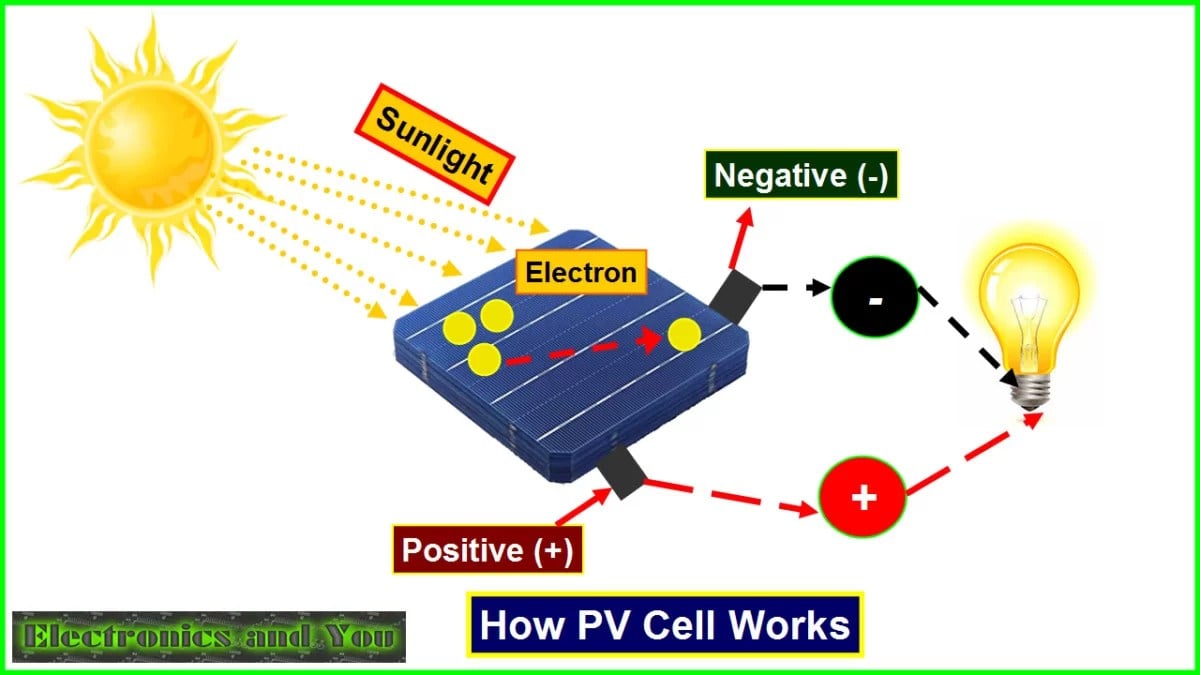
1. Structure of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are typically made of semiconductor materials such as silicon. They are composed of two layers: a P-type layer that contains positively charged “holes” and an N-type layer that contains negatively charged electrons. When photons from sunlight strike the semiconductor material, they transfer their energy to the electrons in the material, allowing them to flow and create an electric current.
2. The Photovoltaic Effect
When light energy is absorbed by the semiconductor material, it excites the electrons, causing them to break free from their atoms and flow through the material. This flow of electrons creates an electric current, which can then be harnessed and used as electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect, and it is the fundamental principle behind how photovoltaic cells generate electricity.
3. Direct Current (DC) Output
Once the photovoltaic cells generate an electric current, it is in the form of direct current (DC) electricity. This type of electricity flows in one direction, which is suitable for use in some electronic devices. However, most household and commercial electrical systems use alternating current (AC) electricity, so the DC electricity produced by the photovoltaic cells must be converted into AC electricity through an inverter before it can be used in buildings and appliances.

4. Connection in Solar Panels
Photovoltaic cells are connected together in solar panels to create larger units of electricity generation. This allows for a higher power output and more efficient use of the sunlight. The electrical connections between the cells in the solar panel enable the combined electric current to be harnessed and utilized for various applications, from small solar-powered devices to large-scale solar energy systems.
5. Environmental Benefits
One of the greatest advantages of photovoltaic cells is their ability to generate electricity without producing any harmful emissions. Unlike traditional fossil fuel-based power plants, photovoltaic cells harness clean and abundant sunlight to generate electricity. This makes them an environmentally friendly and sustainable source of energy, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the mitigation of climate change.
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect, which involves the conversion of sunlight into an electric current in semiconductor materials. This clean and renewable form of energy generation offers numerous environmental and economic benefits, making it a key component of the transition to a more sustainable energy future.

