How Photovoltaic System Works
Introduction to Photovoltaic Systems
Photovoltaic systems, also known as solar photovoltaic systems, are a renewable energy technology that harnesses the power of sunlight to generate electricity. These systems utilize solar panels made up of photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight directly into electricity.
The Function of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are made of semiconductor materials such as silicon. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites the electrons within the semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect, which is the foundation of how photovoltaic systems work.
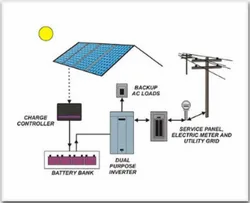
The Components of a Photovoltaic System
A typical photovoltaic system consists of several key components, including solar panels, inverters, storage batteries, and a power meter. Solar panels are installed on rooftops or open ground to capture sunlight, while inverters convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity suitable for use in homes or businesses.
The Working Mechanism of Photovoltaic Systems
When sunlight strikes the solar panels, the photovoltaic cells within the panels generate a direct current (DC) electric current. This electrical energy then travels to the inverters, where it is converted into alternating current (AC) electricity, the form of electricity used in most homes and businesses.
Utilizing Solar Electricity
The AC electricity produced by the photovoltaic system can be used to power appliances, lighting, and electrical devices in the home or business. Any excess electricity generated can be stored in batteries for later use or exported to the grid for credit through a net metering arrangement.
Net Metering and Grid Connection
Photovoltaic systems can be connected to the electrical grid, allowing the excess electricity produced to be fed back into the grid. This process is known as net metering, where the electricity generated by the photovoltaic system offsets the electricity used from the grid, resulting in lower energy bills.
Environmental Benefits of Photovoltaic Systems
Photovoltaic systems offer several environmental benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of sunlight, photovoltaic systems contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
In conclusion, photovoltaic systems work by capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. These systems offer a renewable and clean energy solution that can help reduce electricity costs and environmental impact. With ongoing advancements in solar technology, photovoltaic systems continue to play a crucial role in our transition to a more sustainable energy future.

