How Photovoltaic System Works

Introduction to Photovoltaic System
Photovoltaic system, also known as solar power system, converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that create an electric field when exposed to sunlight. This electric field causes the electrons to move, generating electricity.1. Sunlight Absorption
The first step in the process of how a photovoltaic system works is the absorption of sunlight by the photovoltaic cells. Sunlight is made up of tiny packets of energy called photons. When these photons hit the surface of the solar cells, they excite the electrons in the semiconductor material.2. Electron Movement
The excited electrons create an electric field within the cells, causing them to move. This movement of electrons creates a flow of electricity, which can be harnessed and used as power.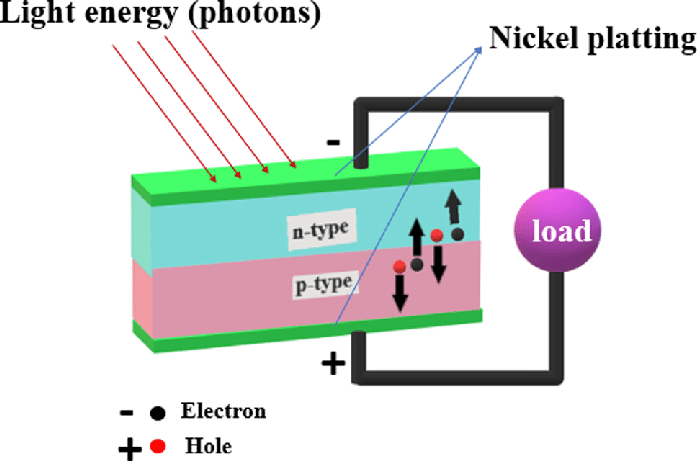
3. Electricity Generation
The flowing electricity is then captured by the wiring within the solar panels and directed to an inverter. The inverter converts the electricity from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses.4. Power Usage
After the electricity is converted to AC, it can be used to power appliances, lights, and other electrical devices in the building where the photovoltaic system is installed. Any excess electricity that is generated can be fed back into the grid or stored in batteries for later use.5. Environmental Benefits
The photovoltaic system works without emitting any greenhouse gases or other pollutants, making it an environmentally friendly energy source. It reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and helps to combat climate change.In conclusion, photovoltaic systems work by harnessing the power of sunlight and converting it into electricity through the use of photovoltaic cells. This clean and sustainable energy source is becoming increasingly popular as the world transitions towards greener and more sustainable energy solutions.

