How Photovoltaic Systems Work: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Introduction
In a world where renewable energy is becoming increasingly important, photovoltaic systems have emerged as a popular and efficient way to generate electricity. But how exactly do these systems work? In this article, we will explore the inner workings of photovoltaic systems and how they harness the power of the sun to produce clean and sustainable energy.
The Basics of Photovoltaic Systems
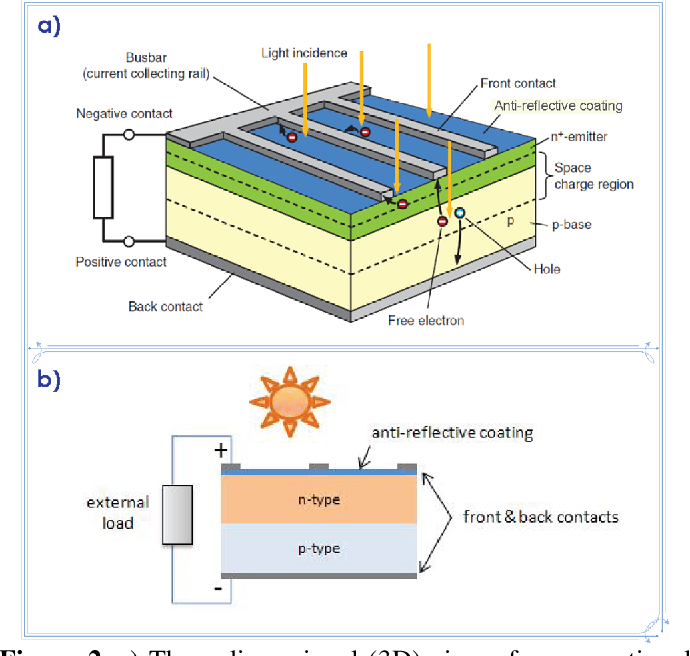
Photovoltaic systems, also known as solar panels, are composed of individual solar cells that convert sunlight into electricity. These cells are typically made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, and are capable of producing direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
1. Sunlight is Converted into Electricity
When sunlight hits the solar cells, the photons in the light excite the electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to flow and create an electric current. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect and is the basis for how photovoltaic systems generate electricity.
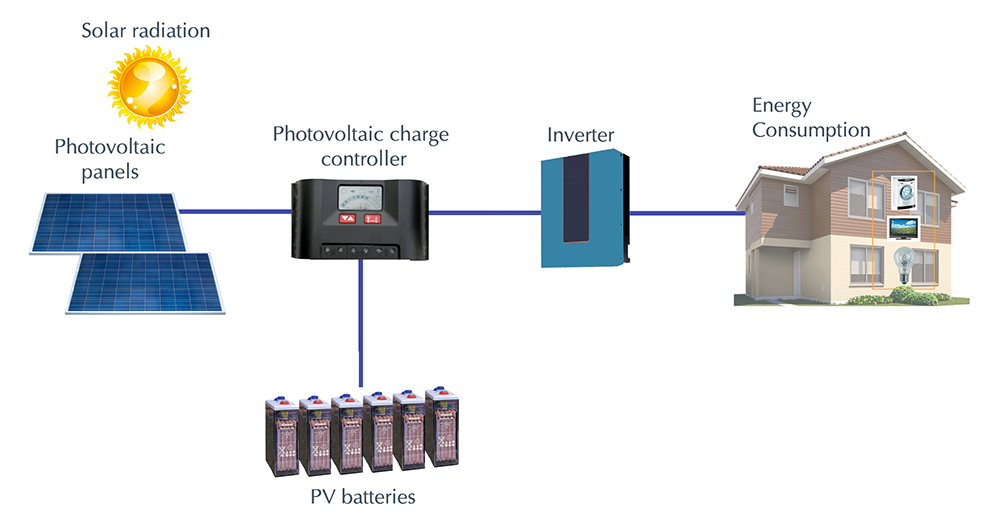
2. Inverter Converts DC to AC Electricity
The direct current generated by the solar cells is then sent to an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is the type of electricity used to power our homes and businesses, making the inverter an essential component of photovoltaic systems.
Utilizing the Generated Electricity
Once the electricity has been converted into AC, it can be used to power electrical devices and appliances. Any excess electricity that is not immediately used can be stored in batteries for later use or sent back to the grid for credit through a process known as net metering.
3. Net Metering and Grid Connection
In many cases, photovoltaic system owners are able to connect to the electrical grid and sell any excess electricity they generate back to the utility company. This not only allows for greater energy independence, but also provides a financial incentive for investing in photovoltaic systems.
4. Environmental Benefits
One of the key advantages of photovoltaic systems is their environmental benefits. By harnessing the power of the sun, these systems produce clean and sustainable energy, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
5. Maintenance and Longevity
Photovoltaic systems require relatively little maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a cost-effective and reliable source of electricity. With proper care and occasional cleaning, solar panels can last for decades and continue to produce electricity efficiently.
Conclusion
In summary, photovoltaic systems work by converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, and then utilizing that electricity to power our homes and businesses. With the ability to connect to the grid and store excess electricity, as well as their environmental benefits and longevity, photovoltaic systems are an increasingly popular choice for generating clean and sustainable energy. As technology continues to improve, it is likely that photovoltaic systems will play an even greater role in the future of renewable energy.



