How Photovoltaics Work

Introduction
Photovoltaics, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light energy directly into electricity. They have many applications, including powering homes, businesses, and even satellites in space. In this article, we will explore the working principle of photovoltaics and how they generate electricity.
Working Principle
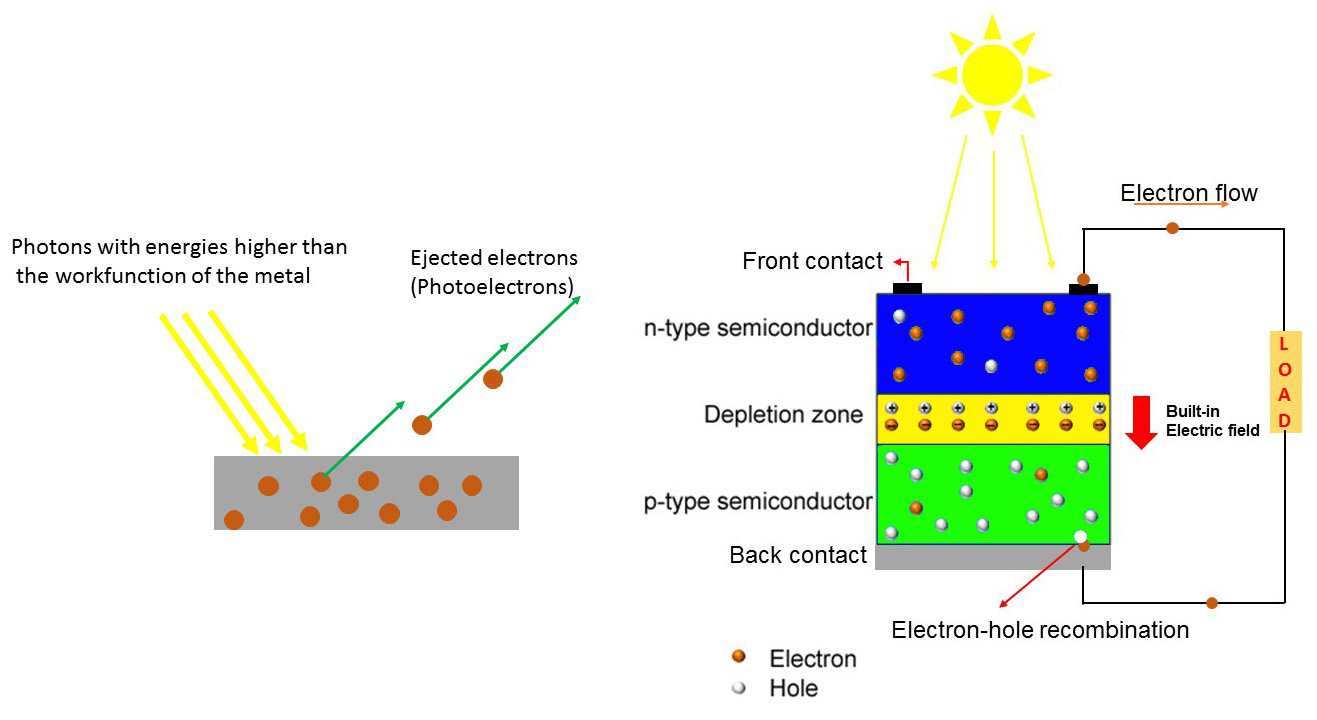
When light photons strike a photovoltaic cell, they are absorbed by the semiconductor material, causing the release of electrons. This process creates an electric current, which can then be harnessed as electricity. The most commonly used semiconductor material in photovoltaics is silicon, due to its abundance and efficiency in converting light into electricity.
Key Components
1. Photovoltaic Cell: This is the basic building block of a solar panel and is responsible for converting sunlight into electricity.
2. Solar Panel: A collection of photovoltaic cells interconnected to form a larger unit that can generate enough electricity to be useful.
3. Inverter: Converts the direct current (DC) electricity from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used in homes and businesses.
Types of Photovoltaics
1. Monocrystalline: Made from a single crystal structure, these solar cells offer high efficiency but are also more expensive to produce.
2. Polycrystalline: These solar cells are made from multiple crystalline structures, which makes them slightly less efficient but more affordable.
3. Thin-film: These solar cells are made by depositing thin layers of semiconductor materials onto a substrate, making them lightweight and flexible, but also less efficient.
Applications
1. Residential: Photovoltaic systems can be installed on rooftops to provide electricity for homes, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering energy costs.
2. Commercial: Many businesses are investing in photovoltaic systems to offset their energy usage and reduce their carbon footprint.
3. Remote Areas: Photovoltaics are being used to provide electricity in remote areas where access to the grid is limited or non-existent.
4. Space: Photovoltaic systems are also used to power satellites and spacecraft in space, where traditional energy sources are not feasible.
Conclusion
Photovoltaics play a crucial role in transitioning towards a sustainable and renewable energy future. Understanding how they work and their various applications is essential for harnessing their full potential and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. As technology continues to advance, photovoltaics will likely become even more efficient and cost-effective, making them an increasingly attractive option for meeting our energy needs.



