How Solar Photovoltaic Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Introduction to Solar Photovoltaic Technology
Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology is a clean and renewable energy source that harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity. This innovative technology has gained widespread popularity in recent years due to its environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we will explore how solar photovoltaic works, from the initial absorption of sunlight to the conversion of solar energy into electrical power.
Solar Photovoltaic Cells: The Building Blocks

At the heart of solar PV technology are the solar photovoltaic cells, also known as solar panels. These cells are made from semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which have the unique ability to convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the surface of the solar panels, the energy from the photons in the sunlight is transferred to the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating an electric current.
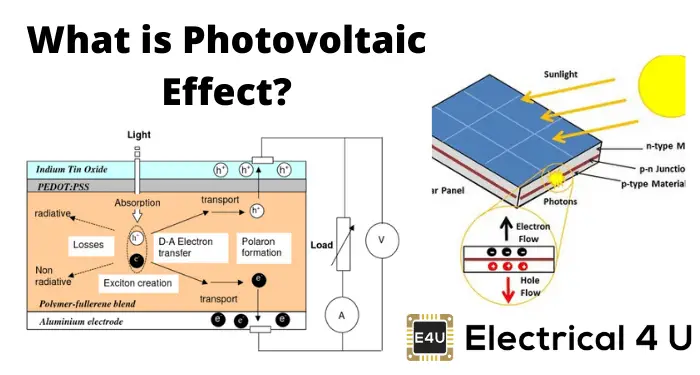
The Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is the process by which sunlight is converted into electricity. When photons from the sun strike the surface of the solar panels, they knock electrons loose from the semiconductor material. These electrons then flow through the material, creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) electricity is then captured and converted into alternating current (AC) electricity through an inverter, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and other electrical devices.
Grid-Tied and Off-Grid Systems
Solar photovoltaic systems can be connected to the electricity grid or operate independently as off-grid systems. In grid-tied systems, any excess electricity generated by the solar panels can be fed back into the grid, allowing homeowners and businesses to earn credits for the power they produce. Off-grid systems, on the other hand, rely on battery storage to store excess electricity for use when sunlight is not available.
The Role of Inverters
Inverters play a crucial role in the solar PV system by converting the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity that can be used to power electrical devices. This process enables the solar power to be compatible with the grid and ensures that it can be efficiently used in homes and businesses. In addition, inverters also monitor the performance of the solar PV system and can provide valuable data on energy production and system efficiency.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of the solar PV system are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes checking the condition of the solar panels, cleaning any debris or dirt that may accumulate on the surface, and inspecting the electrical components for any signs of wear or damage. By keeping the system well-maintained, homeowners and businesses can maximize the energy output and extend the lifespan of their solar PV system.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
The use of solar photovoltaic technology offers a wide range of environmental and economic benefits. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar PV systems produce clean and renewable energy, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. In addition, homeowners and businesses can benefit from significant cost savings on their electricity bills and may even be eligible for incentives and rebates for installing solar PV systems.
In conclusion, solar photovoltaic technology offers a sustainable and efficient way to generate electricity from the sun’s abundant energy. By understanding how solar photovoltaic works, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about harnessing the power of solar energy to meet their electricity needs. With the continued advancements in solar PV technology, the future looks bright for clean and renewable energy solutions.

