How to Calculate Duty Cycle for Photovoltaic Panels
When it comes to photovoltaic panels, understanding the duty cycle is crucial for maximizing their efficiency and effectiveness. The duty cycle refers to the amount of time the panel is actively generating electricity compared to the total time it is exposed to sunlight. Calculating the duty cycle for photovoltaic panels involves a few key steps and considerations. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to calculate the duty cycle for photovoltaic panels.
Understanding Duty Cycle
The duty cycle of a photovoltaic panel is a measure of its operational efficiency. It is expressed as a percentage and represents the amount of time the panel is generating electricity over a defined time period, typically a day, week, or month. A higher duty cycle indicates that the panel is producing electricity for a larger portion of the time it is exposed to sunlight, resulting in greater energy output.
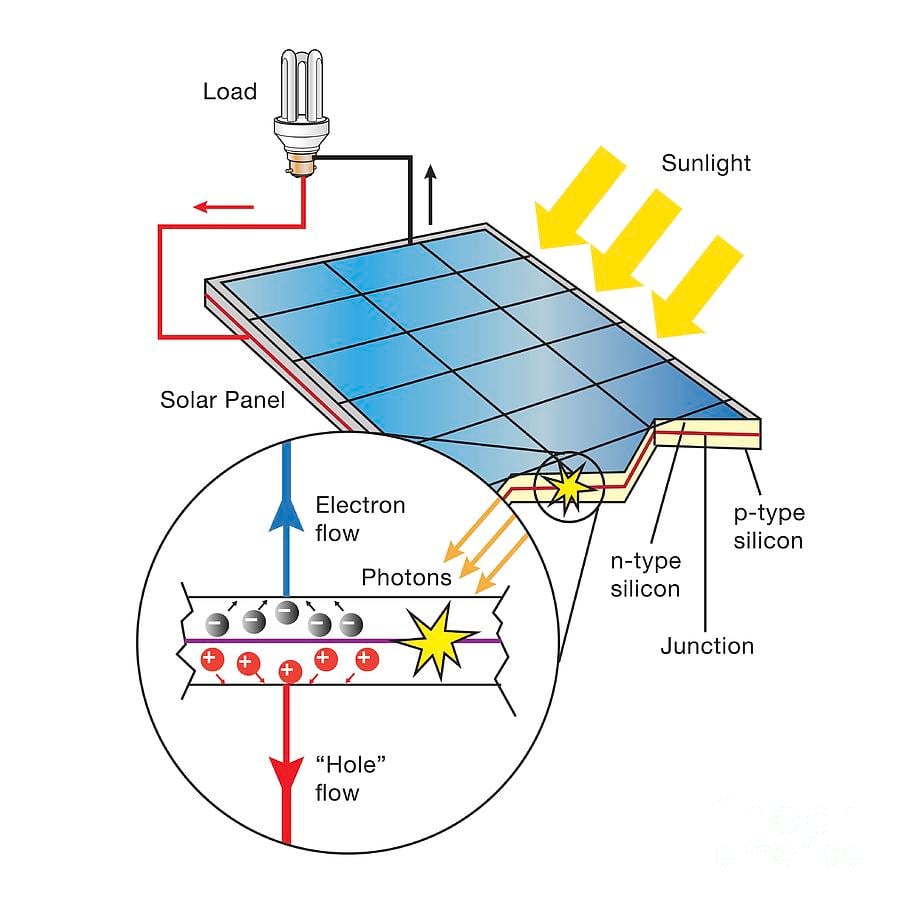
Factors Affecting Duty Cycle
Several factors can influence the duty cycle of photovoltaic panels, including:
Sunlight Intensity:
Higher sunlight intensity can increase the duty cycle as the panel receives more energy to convert into electricity.Panel Orientation:
The orientation of the panel relative to the sun’s path affects the duration of sunlight exposure and, consequently, the duty cycle.Weather Conditions:
Cloud cover, precipitation, and other weather factors can impact the amount of sunlight reaching the panel, influencing its duty cycle.Geographic Location:
The latitude and climate of the panel’s installation location play a significant role in determining the duty cycle.Tracking Systems:
Trackers that adjust the position of the panel to follow the sun can enhance the duty cycle by maximizing sunlight capture.Calculating Duty Cycle
To calculate the duty cycle for photovoltaic panels, follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine Active and Total Sunlight Hours
First, identify the total hours of sunlight exposure for a specific time period, such as a day or a month. Then, determine the number of hours the panel actively generates electricity during the same period. This information can be obtained from monitoring systems or solar irradiance data for the location.
Step 2: Calculate Duty Cycle
Once you have the active and total sunlight hours, use the following formula to calculate the duty cycle:
Duty Cycle = (Active Sunlight Hours / Total Sunlight Hours) * 100%
For example, if a photovoltaic panel generates electricity for 6 hours out of a total of 12 hours of sunlight exposure in a day, the duty cycle would be:
Duty Cycle = (6 hours / 12 hours) * 100% = 50%
In this case, the panel has a duty cycle of 50%, meaning it is actively producing electricity for half of the total sunlight hours.
Optimizing Duty Cycle
To optimize the duty cycle of photovoltaic panels, consider the following strategies:
Efficient Panel Placement:
Install panels in locations with maximum sunlight exposure and proper orientation.Use Tracking Systems:
Implement tracking systems that follow the sun’s path to increase panel efficiency.Regular Maintenance:
Keep panels clean and free of obstructions to ensure optimal sunlight capture.Monitoring and Analysis:
Regularly monitor panel performance and analyze duty cycle data to identify areas for improvement.In conclusion, understanding and calculating the duty cycle for photovoltaic panels is essential for optimizing their energy production. By considering various factors and following the calculation process outlined in this article, you can assess and improve the duty cycle of photovoltaic panels, leading to increased efficiency and energy output.

