Is Battery Storage Expensive for Grid? Understanding the Costs and Benefits

The Cost of Battery Storage for the Grid
There is a common misconception that battery storage for the grid is expensive. However, the costs of battery storage have been steadily declining in recent years. According to a report by Bloomberg NEF, the cost of lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in grid storage, has fallen by 87% since 2010. This significant decrease in cost has made battery storage a more viable option for grid operators.Factors Affecting the Cost of Battery Storage
Several factors can affect the cost of battery storage for the grid. The size and capacity of the battery system, the technology used, and the specific requirements of the grid all play a role in determining the overall cost. Additionally, the cost of materials and components, as well as installation and maintenance expenses, must be taken into consideration.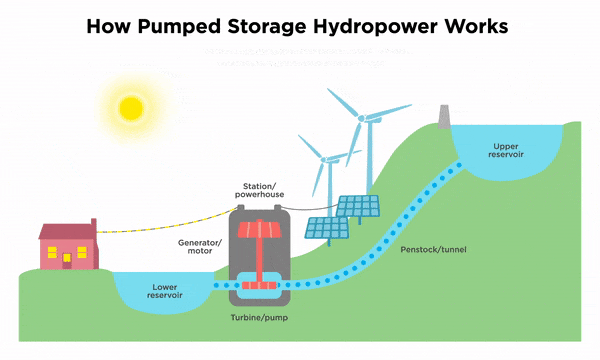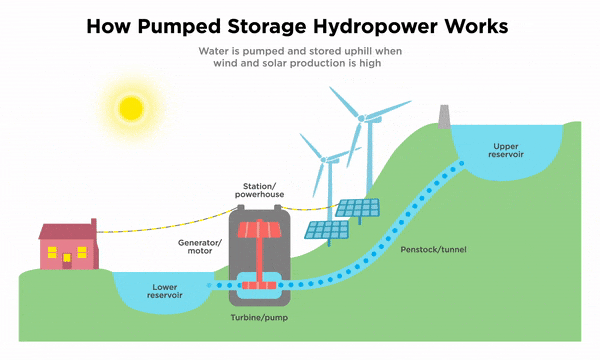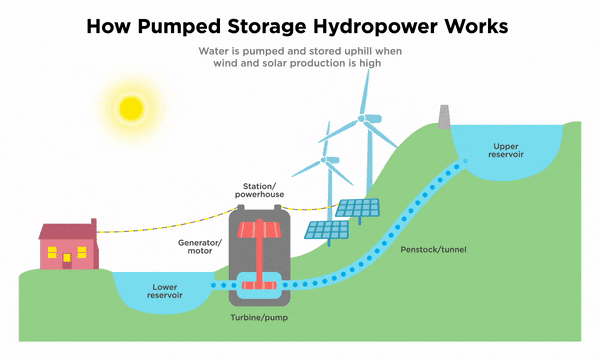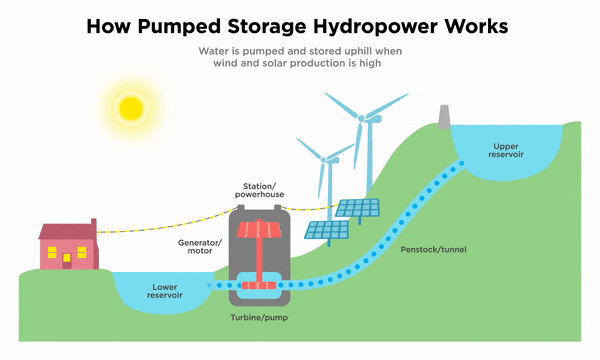
The Benefits of Battery Storage for the Grid
While the initial cost of implementing battery storage for the grid may be significant, there are numerous benefits that can make it a worthwhile investment. Battery storage can help improve grid reliability and stability by providing backup power during outages and addressing peak demand periods. It can also facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, by storing excess energy for use when generation is low.1. Technology and Innovation
Advancements in battery technology and ongoing innovation in the industry have contributed to the declining costs of battery storage for the grid. New developments, such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries, have the potential to further reduce costs and improve performance, making battery storage an even more attractive option for grid operators.2. Environmental Benefits
In addition to the economic advantages, battery storage for the grid also offers environmental benefits. By enabling the integration of renewable energy sources, battery storage can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change. This aligns with the growing global focus on sustainability and clean energy.3. Long-Term Savings
While the upfront costs of battery storage may be a concern for some grid operators, it’s important to consider the long-term savings that can be achieved. By reducing reliance on expensive peaking power plants and avoiding the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades, battery storage can ultimately lead to cost savings for utilities and consumers.4. Grid Resilience and Security
Battery storage can enhance grid resilience and security by providing a reliable source of backup power during emergencies and natural disasters. This capability is particularly important as extreme weather events become more frequent, posing significant challenges to grid reliability.5. Policy and Regulatory Support
Government policies and regulations can also play a crucial role in making battery storage for the grid more affordable. Incentives, subsidies, and supportive frameworks can encourage investment in battery storage projects and help offset initial costs, making it a more viable option for utilities and grid operators.In conclusion, while the upfront costs of battery storage for the grid may have been a barrier in the past, the declining costs, technological advancements, and numerous benefits make it an increasingly attractive option. As the industry continues to evolve and innovate, battery storage is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of grid management and the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy system.


