Is Battery Storage Spinning or Nonspinning Reserve?
When it comes to reserve capacity in the energy industry, battery storage plays a crucial role. But what exactly is the difference between spinning and nonspinning reserve when it comes to battery storage? In this article, we will explore the two types of reserve capacity and how they relate to battery storage.
Spinning Reserve
Spinning reserve refers to the capacity that is immediately available to the grid in case of a sudden increase in demand or unexpected generator outage. In the past, spinning reserve was provided by traditional power plants that were kept running at less than full capacity in order to respond quickly to fluctuations in demand. However, with the rise of battery storage technology, spinning reserve can now be provided by batteries that are charged and ready to discharge at a moment’s notice.
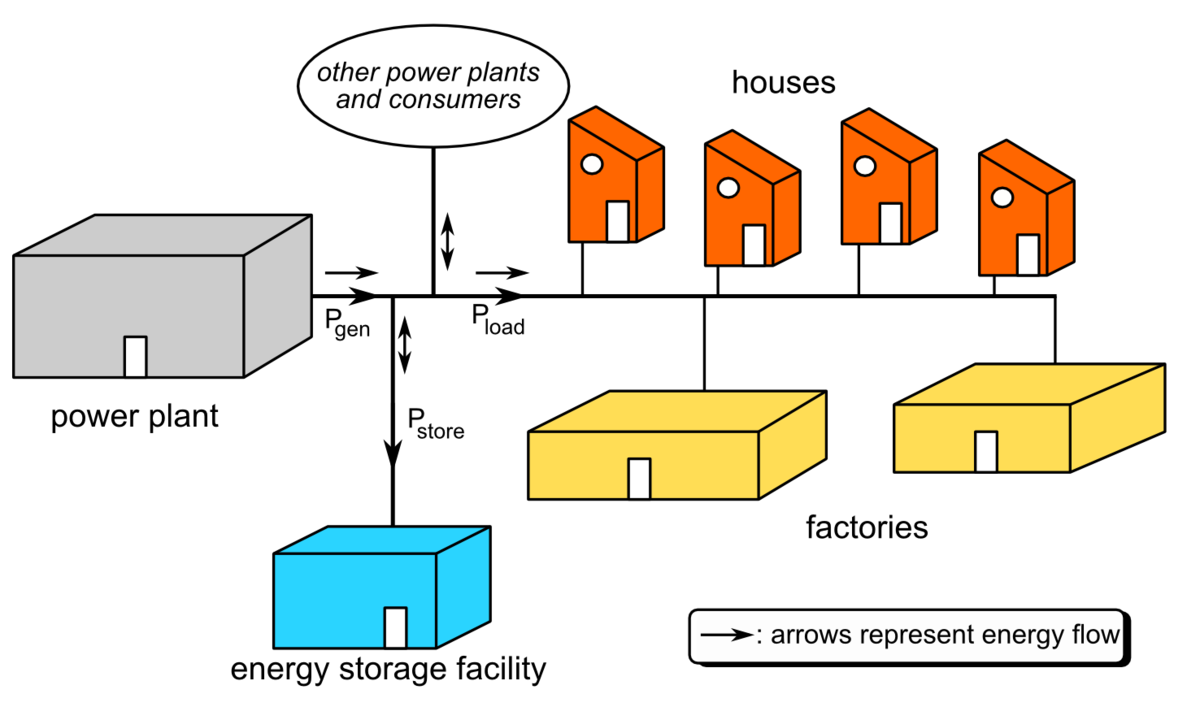
Battery Storage for Spinning Reserve
Battery storage is an ideal solution for providing spinning reserve capacity due to its ability to charge and discharge quickly. In the event of a sudden increase in demand or generator outage, batteries can respond almost instantaneously, providing the necessary power to stabilize the grid. This not only helps to maintain grid stability but also ensures a reliable power supply for consumers.
Benefits of Battery Storage for Spinning Reserve
There are several benefits to using battery storage for spinning reserve capacity. Firstly, batteries can be located closer to areas of high demand, reducing the need for long transmission lines and improving grid reliability. Additionally, battery storage can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing reserve requirements, providing flexibility and cost savings for grid operators.
Nonspinning Reserve
Nonspinning reserve, on the other hand, refers to the capacity that is available to the grid but requires some time to ramp up before it can be used. This type of reserve is typically provided by power plants that are not running but can be brought online within a certain time frame. In the past, nonspinning reserve was provided by coal or gas-fired power plants, but battery storage is increasingly being used to provide this type of reserve capacity as well.
Battery Storage for Nonspinning Reserve
Battery storage can also be used to provide nonspinning reserve capacity by charging during periods of low demand and discharging when needed. While batteries may not be able to respond as quickly as traditional spinning reserve sources, they can still provide a reliable and efficient solution for grid operators. In some cases, battery storage may even be able to provide a combination of spinning and nonspinning reserve capacity, offering even greater flexibility to the grid.
Conclusion
In conclusion, battery storage plays a crucial role in providing both spinning and nonspinning reserve capacity to the grid. With its ability to charge and discharge quickly, battery storage is an ideal solution for stabilizing the grid and ensuring a reliable power supply for consumers. As the energy industry continues to evolve, it is likely that battery storage will play an increasingly important role in meeting reserve capacity requirements.




