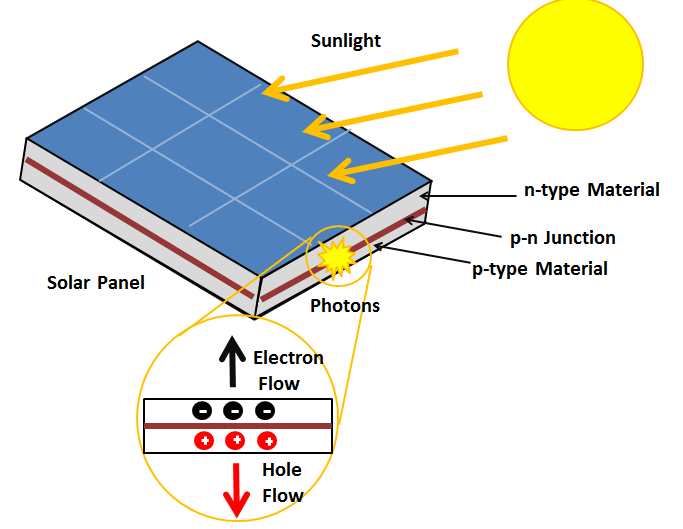
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. These cells are made from a variety of materials, each with its own unique properties and benefits. In this article, we’ll explore the different materials used to make photovoltaic cells and how they work to generate clean, sustainable energy.
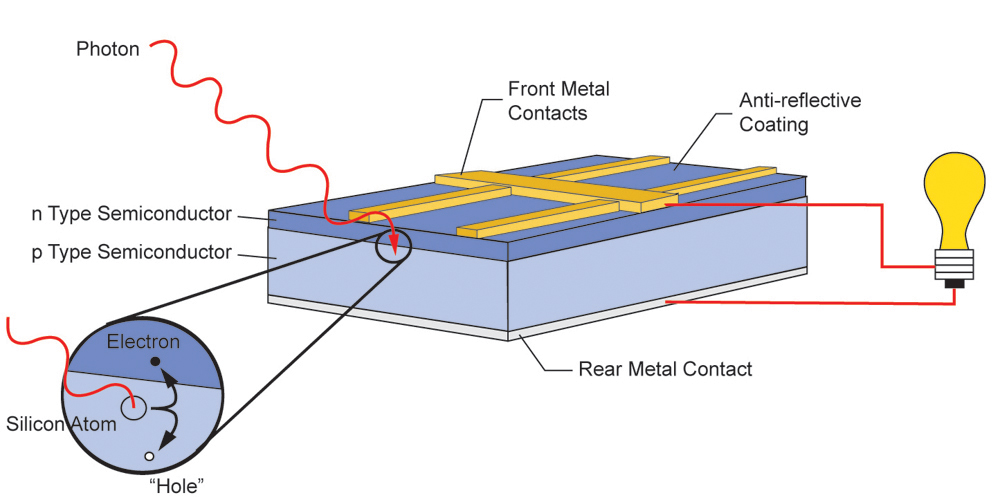
Silicon Photovoltaic Cells
Silicon is the most commonly used material in photovoltaic cells. It is abundant, inexpensive, and has the ability to absorb sunlight effectively. Silicon cells are typically made from either monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon, with monocrystalline cells being more efficient but also more expensive to produce. These cells work by using the sunlight to create an electrical imbalance, which then produces a flow of electricity.Thin-Film Photovoltaic Cells
Thin-film photovoltaic cells are made from a variety of materials, including cadmium telluride, copper indium gallium diselenide, and amorphous silicon. These cells are more flexible and lightweight than traditional silicon cells, making them suitable for a wider range of applications. While thin-film cells may not be as efficient as silicon cells, they are often more cost-effective and can be used in areas with limited space or unconventional installation requirements.Perovskite Photovoltaic Cells
Perovskite is a relatively new material in the field of photovoltaics, but it has shown great potential for producing highly efficient and low-cost solar cells. Perovskite cells can be made using simple manufacturing processes and have demonstrated efficiency levels that rival traditional silicon cells. However, there are still challenges to be addressed in terms of stability and long-term performance.