Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are the heart of solar power systems. These cells are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity, making them a crucial component of renewable energy production. But what are photovoltaic cells made up of, and how do they work? In this article, we will explore the composition and functionality of these vital components.
Composition of Photovoltaic Cells
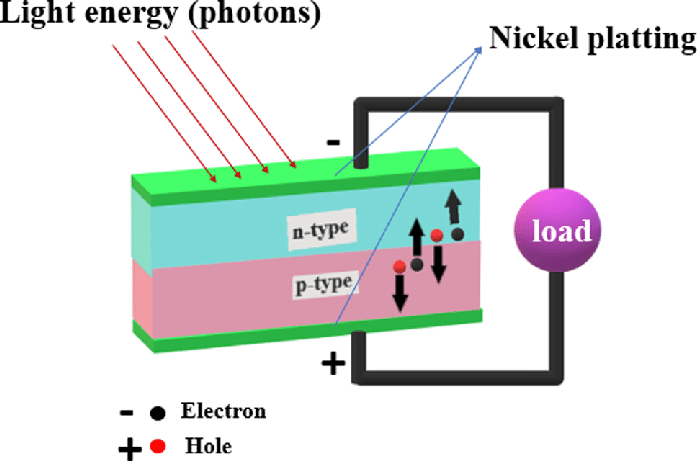
Photovoltaic cells are typically made up of semiconductor materials such as silicon. These materials have unique properties that allow them to convert light energy into electrical energy. In order to create a functioning solar cell, the semiconductor material is treated with various dopants and coatings to enhance its ability to generate electricity when exposed to sunlight.The Role of Silicon
Silicon is the most commonly used material in photovoltaic cells due to its abundance and favorable properties for solar energy production. When light photons strike the silicon, they excite the electrons within the material, creating an imbalance of charge that can be harnessed to produce an electric current.Other Components
In addition to the semiconductor material, photovoltaic cells also include metal conductors to facilitate the movement of the generated electricity, as well as an anti-reflective coating to maximize light absorption. The cells are typically encased in a protective material, such as glass, to shield them from the elements while still allowing sunlight to penetrate.
How Photovoltaic Cells Work
When sunlight strikes the surface of a photovoltaic cell, the energy from the photons is absorbed by the semiconductor material, causing the release of electrons. These electrons are then captured and directed by the metal conductors, creating a flow of electricity. This direct current (DC) electricity can then be converted into alternating current (AC) using an inverter for use in homes and businesses.Efficiency and Output
The efficiency of a photovoltaic cell refers to the amount of sunlight it can convert into electricity. Higher efficiency cells are capable of generating more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, making them more desirable for solar power applications. Additionally, the output of a photovoltaic cell depends on factors such as the angle of sunlight, temperature, and shading.Advancements in Photovoltaic Technology
Research and development efforts in the field of photovoltaics have led to significant advancements in cell design and efficiency. New materials and manufacturing techniques are constantly being explored to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of solar cells. These innovations are driving the widespread adoption of solar power as a clean and sustainable energy source.In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are composed of semiconductor materials, metal conductors, and protective coatings, all working together to convert sunlight into electricity. The advancements in photovoltaic technology continue to make solar power an increasingly viable and accessible renewable energy solution. With ongoing research and development, the future looks bright for the widespread use of photovoltaic cells in solar energy systems.

