Solar photovoltaics, also known as solar PV, is a technology that converts sunlight into electricity by using solar cells. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that absorb photons from the sunlight and generate an electric current.
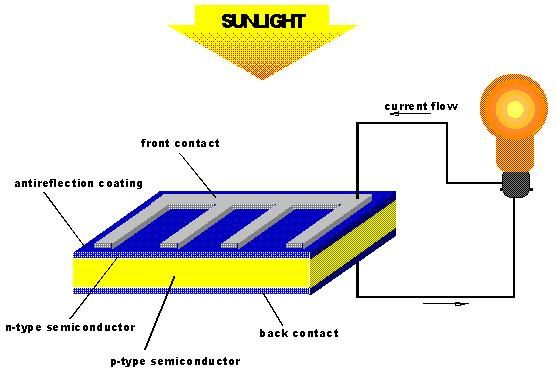
There are two main types of solar photovoltaics: crystalline silicon and thin-film. Crystalline silicon solar panels are the most common and widely used type of solar PV. They are made of silicon wafers that are cut from blocks of silicon crystals. Thin-film solar panels, on the other hand, are made by depositing thin layers of semiconductor materials onto a substrate. While thin-film solar panels are less efficient than crystalline silicon panels, they are cheaper to produce and can be used in a variety of applications.
Solar photovoltaics have many advantages. They produce clean and renewable energy, which helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Solar PV systems are also relatively low maintenance and have a long lifespan, typically lasting for 25 years or more. Additionally, solar panels can be installed on rooftops or in open fields, making them suitable for both residential and commercial use.
In recent years, the cost of solar photovoltaics has been steadily declining, making it an increasingly attractive option for energy generation. Government incentives and rebates for solar installations have also contributed to the growth of the solar PV industry.
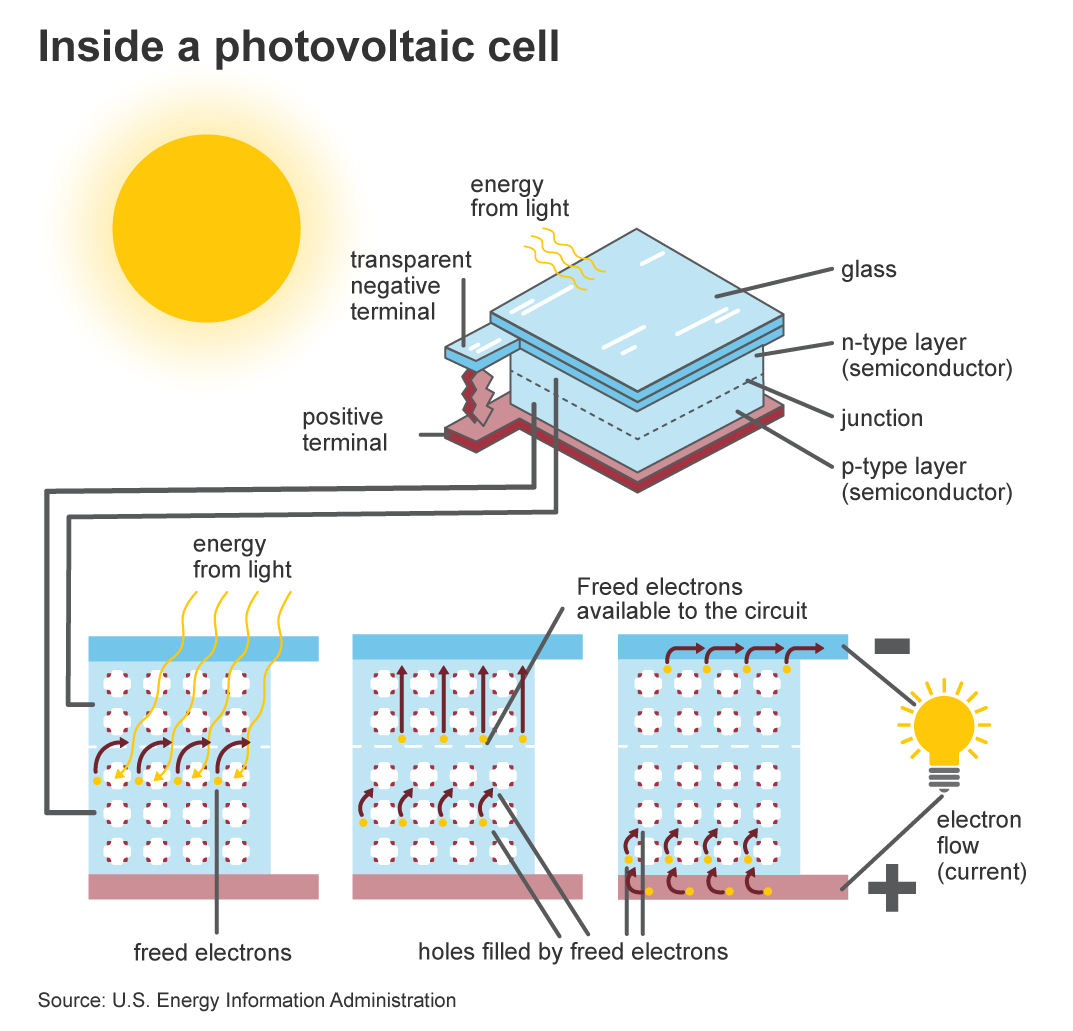
Despite its numerous benefits, there are still challenges facing the widespread adoption of solar photovoltaics. One of the main challenges is the intermittency of sunlight, which limits the reliability of solar energy. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, are being developed to address this issue, but they can add to the overall cost of a solar PV system.
Overall, solar photovoltaics have the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable and clean energy future. As technology continues to advance and costs continue to decrease, solar PV is likely to become an increasingly important source of electricity generation worldwide.

