What are Storage Batteries?
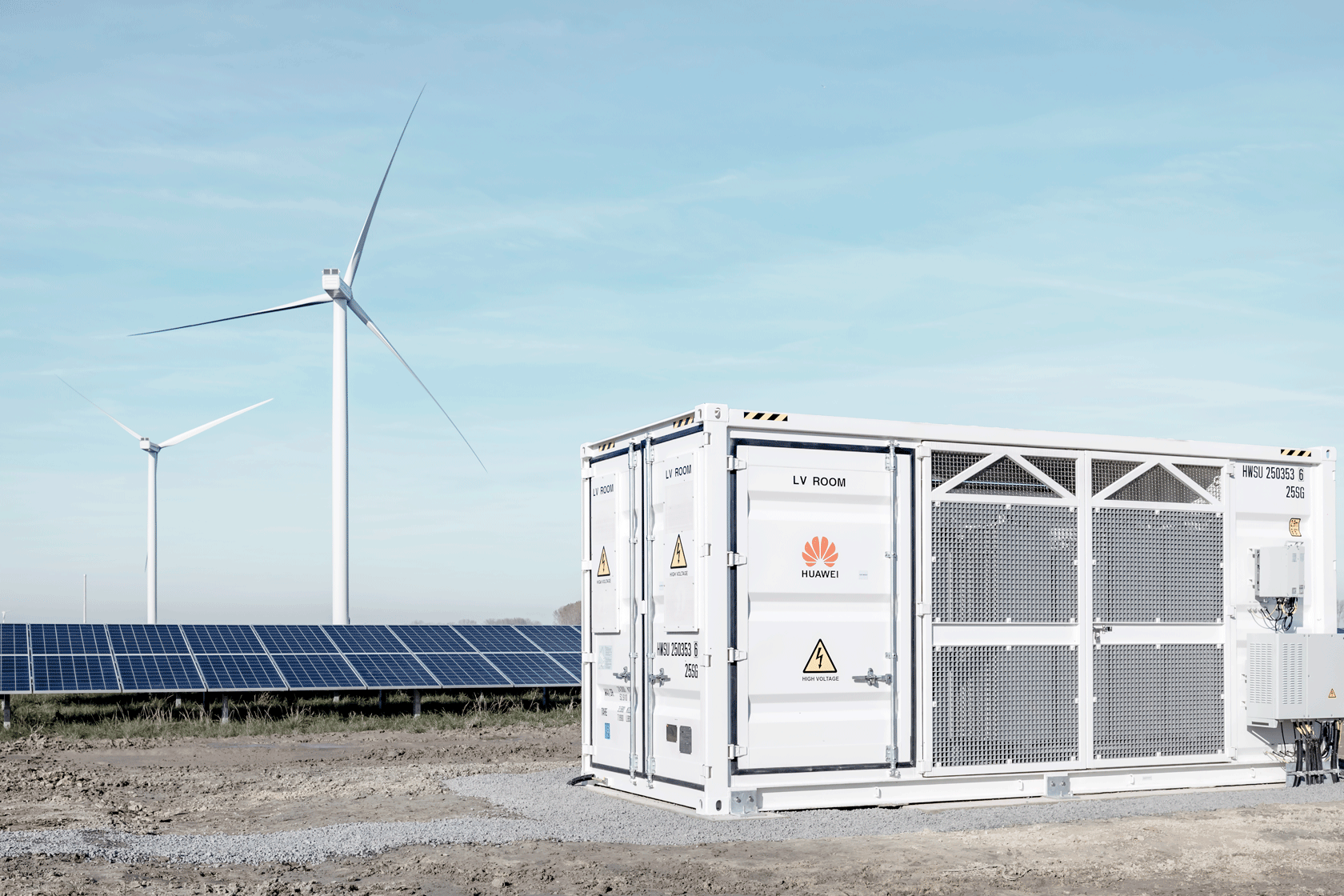
Storage batteries, also known as rechargeable batteries, are devices that store energy through electrochemical reactions and can be used to power a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices to large industrial systems. These batteries are designed to be recharged and reused multiple times, making them an essential component in modern energy storage and power systems.
The Function of Storage Batteries
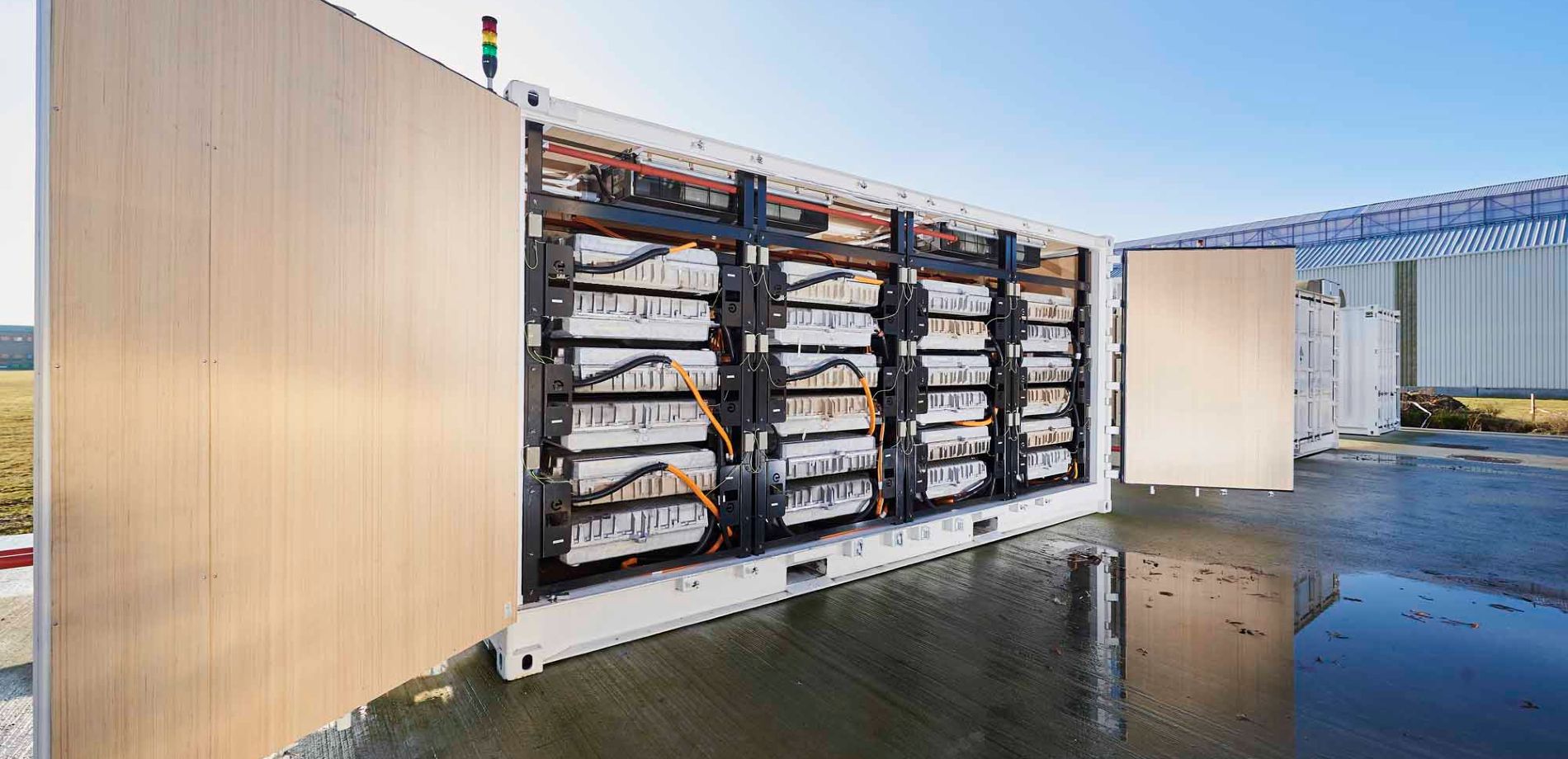

1. Energy Storage
One of the primary functions of storage batteries is to store energy generated from various sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or the electrical grid. This stored energy can then be used to power devices and equipment when the primary energy source is not available.
2. Power Backup
Storage batteries are commonly used as backup power sources for critical systems, such as hospitals, data centers, and telecommunications networks. In the event of a power outage, these batteries can provide a reliable and uninterrupted power supply until the primary power source is restored.
3. Electric Vehicles
With the growing popularity of electric vehicles, storage batteries play a crucial role in powering these vehicles, storing energy from the grid or renewable sources and delivering it to the vehicle’s electric motor when needed.
Types of Storage Batteries
1. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most common types of storage batteries. They are relatively low cost and are used in a wide range of applications, including automotive, industrial, and renewable energy systems.
2. Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become increasingly popular due to their high energy density and long cycle life. They are commonly used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and grid-scale energy storage systems.
3. Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that stores energy in liquid electrolytes. They are well-suited for large-scale energy storage applications, such as renewable energy integration and grid stabilization.
4. Nickel-Based Batteries
Nickel-based batteries, such as nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries, are known for their robustness and reliability. They are commonly used in backup power systems and portable electronic devices.
5. Sodium-Based Batteries
Sodium-based batteries are an emerging technology that shows promise for grid-scale energy storage. They are based on abundant and inexpensive materials, making them a potential cost-effective solution for large-scale energy storage.
Conclusion
Storage batteries are an essential technology for storing and delivering energy in a wide range of applications. With the increasing demand for renewable energy and electric vehicles, the development of advanced and efficient storage battery technologies will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy storage and power systems.


