The Advantages and Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Cells
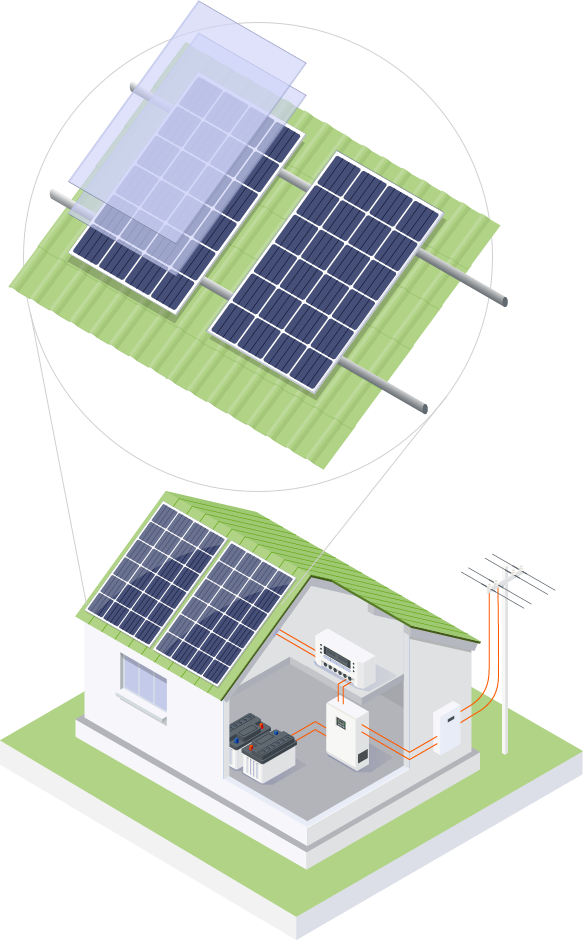
Introduction
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light into electricity. They are an increasingly popular choice for generating renewable energy due to their many advantages. However, like any technology, they also have their drawbacks. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of photovoltaic cells.
Advantages
1. Renewable Energy Source
One of the greatest advantages of photovoltaic cells is that they harness energy from the sun, which is an abundant and renewable resource. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to environmental pollution, solar energy is sustainable and clean.
2. Cost Savings
While the initial investment in solar panels and photovoltaic systems can be expensive, they can ultimately save homeowners and businesses money on their electricity bills. Once installed, photovoltaic cells require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a cost-effective energy solution in the long run.

3. Environmental Benefits
Photovoltaic cells produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This not only reduces carbon emissions and helps combat climate change, but also improves air quality and public health.
4. Versatility
Photovoltaic cells can be integrated into a wide range of applications, from large-scale solar power plants to portable solar chargers for electronic devices. Their versatility makes them suitable for various uses, including off-grid power generation in remote areas.
5. Energy Independence
By generating their own electricity with photovoltaic cells, individuals and businesses can reduce their reliance on the grid and fossil fuels. This can provide greater energy security and stability, especially in regions prone to power outages or energy shortages.
Disadvantages
1. Intermittent Energy Output
One of the main drawbacks of photovoltaic cells is their dependency on sunlight. Cloudy days, nighttime, and other factors can reduce their energy output, making them less reliable than traditional power sources.
2. Energy Storage Challenges
Storing solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight can be challenging and expensive. While advancements in battery technology are improving energy storage capabilities, it remains a limitation for many photovoltaic systems.
3. Land Use and Aesthetics
Large-scale solar power plants and arrays require significant amounts of land, raising concerns about habitat disruption and land use conflicts. Additionally, some people find solar panels to be unattractive or incompatible with the architecture of their homes or businesses.
4. Manufacturing and Recycling
The production of photovoltaic cells involves the use of materials such as silicon, which may have environmental and social impacts. Additionally, the recycling of solar panels at the end of their lifespan poses challenges in terms of efficiency and cost.
5. Initial Costs and ROI
While the long-term savings of solar energy are considerable, the upfront costs of purchasing and installing photovoltaic systems can be prohibitive for some individuals and organizations. The return on investment and payback period can vary depending on factors such as location, incentives, and energy consumption.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic cells offer numerous advantages as a clean and sustainable energy source, but they also have limitations that need to be addressed. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, the potential for photovoltaic cells to play a greater role in our energy future is promising. By carefully considering the benefits and drawbacks, we can make informed decisions about integrating solar energy into our lives and communities.



