Technological Differences between High and Low Voltage Batteries for Home Energy Storage
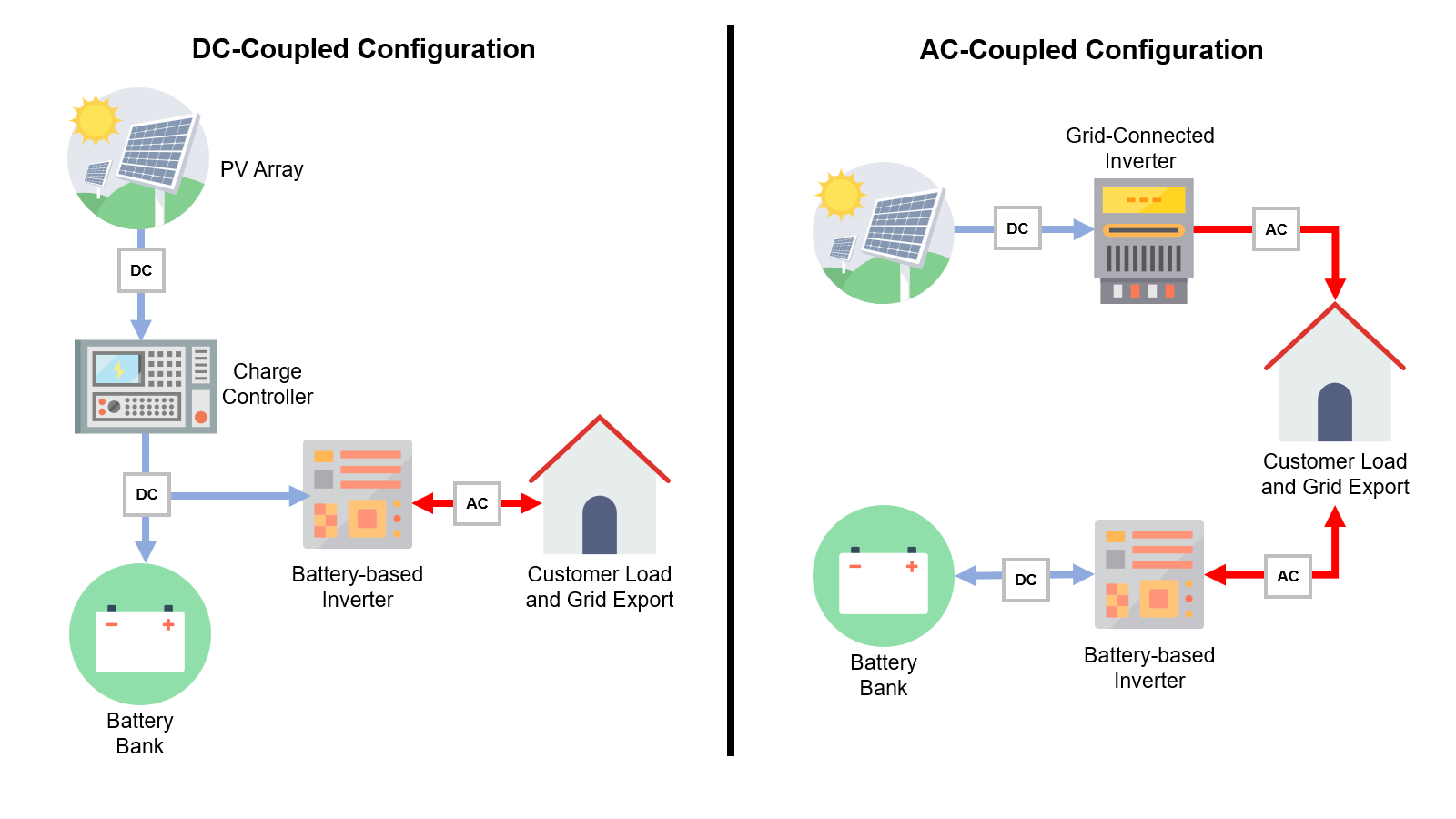
Introduction
When it comes to home energy storage, batteries play a crucial role in storing and releasing energy as needed. High and low voltage batteries are two common options for homeowners looking to implement energy storage solutions. Each type of battery has its own set of technological differences and advantages, making it important for consumers to understand the distinctions before making a decision.
Chemical Composition
High voltage batteries, such as lithium-ion, typically use a higher energy density chemistry, allowing them to store more energy in a smaller space. This results in a smaller and lighter battery pack, making it easier to install and manage. On the other hand, low voltage batteries, like lead-acid, have a lower energy density and therefore require a larger physical footprint to store the same amount of energy.
Efficiency
High voltage batteries generally have higher charge and discharge efficiencies compared to low voltage batteries. This means that they can store and release energy with less loss, resulting in overall higher efficiency in energy storage systems. Low voltage batteries may experience higher self-discharge rates and lower efficiency, making them less suitable for long-term energy storage solutions.
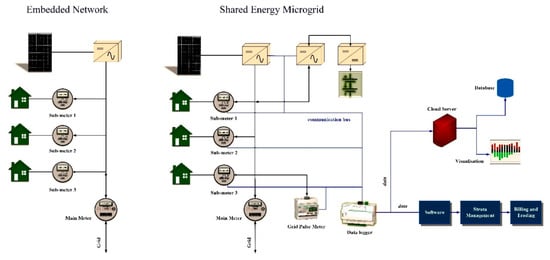
Cost
Due to their advanced chemistry and higher efficiency, high voltage batteries tend to be more expensive upfront compared to low voltage batteries. However, when considering the total cost of ownership over the lifespan of the batteries, high voltage options may actually be more cost-effective. They require less maintenance, have longer lifespans, and offer better performance, ultimately providing better value in the long run.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
High voltage batteries are better suited for integrating with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, due to their higher efficiency and energy density. This allows homeowners to capture and store more energy from these sources, ultimately reducing their reliance on the grid. Low voltage batteries may struggle to meet the demands of such renewable energy systems, making them less ideal for homeowners seeking to go off-grid or reduce their carbon footprint.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the technological differences between high and low voltage batteries for home energy storage are significant. While high voltage batteries offer higher energy density, better efficiency, and integration with renewable energy sources, they come at a higher initial cost. On the other hand, low voltage batteries may be more affordable upfront but could prove to be less effective and efficient in the long run. Homeowners should carefully consider their energy storage needs and goals before making a decision on which type of battery to implement in their energy storage system.



