Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light energy into electricity. They play a crucial role in the production of renewable energy and are widely used in a variety of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large solar power plants. However, there are several factors that can limit the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic cells.
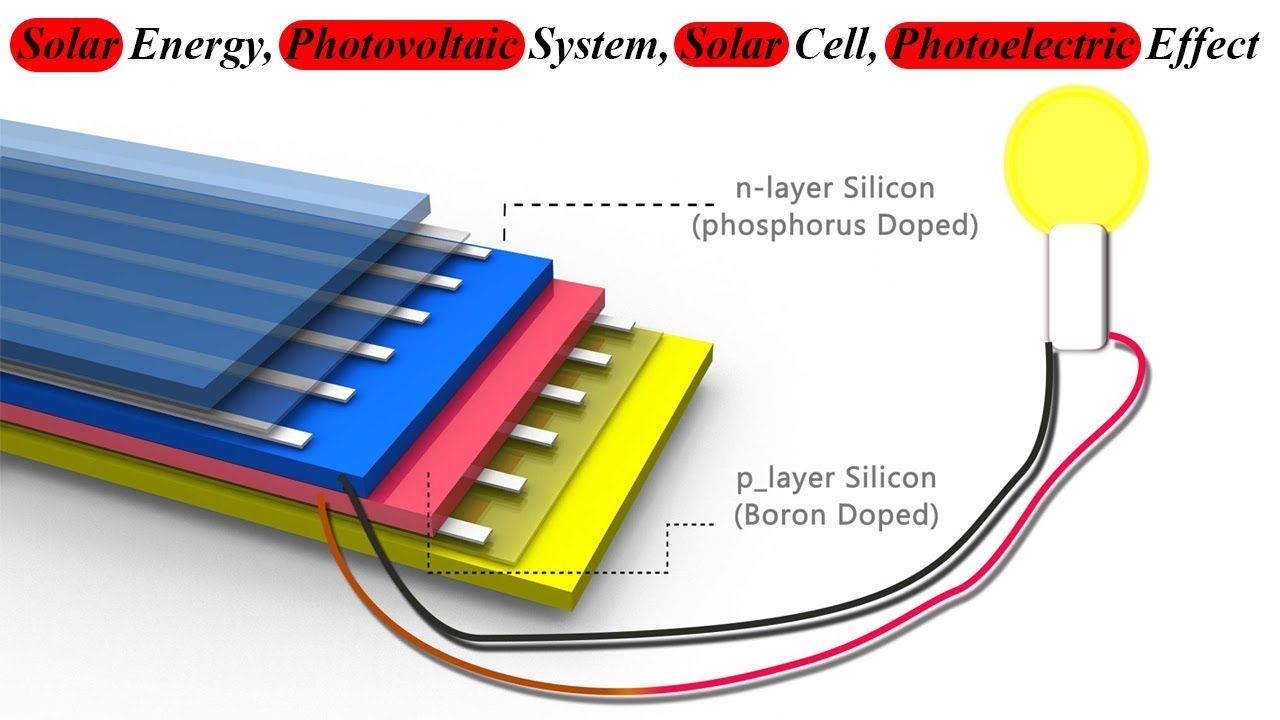
1. Material Limitations The materials used in photovoltaic cells can have a significant impact on their efficiency. For example, some materials may not be able to effectively convert light into electricity, or they may degrade over time, reducing the overall lifespan of the cell. Additionally, the availability and cost of certain materials can limit the scalability and widespread adoption of photovoltaic technology.
2. Environmental Factors Environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, can also have an impact on the performance of photovoltaic cells. High temperatures can reduce the efficiency of solar cells, while humidity and air pollution can cause corrosion and degradation of the cell materials. These factors can limit the effectiveness of photovoltaic systems, particularly in regions with extreme climates or poor air quality.
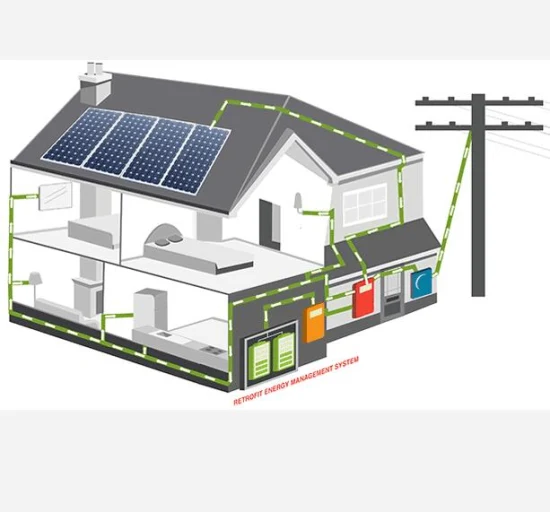
3. Design and Installation The design and installation of photovoltaic systems can also play a role in limiting their performance. Improper placement or orientation of solar panels, as well as shading from nearby structures or vegetation, can reduce the amount of light that reaches the cells and decrease their efficiency. In addition, poor quality installation practices can lead to issues such as electrical losses, poor connectivity, and reduced energy generation.
4. Maintenance and Upkeep Regular maintenance and upkeep are essential for the long-term performance of photovoltaic cells. Dust, dirt, and other debris can accumulate on the surface of solar panels, reducing their ability to capture light and generate electricity. In addition, regular inspections and repairs are necessary to address any potential issues with the cells or the overall system, such as wiring faults or module degradation.
5. External Limitations External factors, such as government regulations, market dynamics, and competing technologies, can also limit the growth and adoption of photovoltaic cells. For example, changing policies and financial incentives for solar energy can impact the economics of photovoltaic systems, while the development of alternative energy sources can create competition for solar technology.
In conclusion, while photovoltaic cells have the potential to play a significant role in the transition to renewable energy, there are several factors that can limit their efficiency and performance. By addressing these limitations through research, innovation, and policy support, we can work towards maximizing the potential of photovoltaic technology and its contribution to a sustainable energy future.

