What is a Photovoltaic Cell and How Does it Work?
A photovoltaic cell, also known as a solar cell, is a device that converts sunlight into electrical energy. It is a key component in solar panels, which are used to generate electricity from the sun’s energy. Photovoltaic cells are made from materials such as silicon, which are capable of absorbing photons (light particles) and releasing electrons. These electrons are then captured and converted into usable electricity.
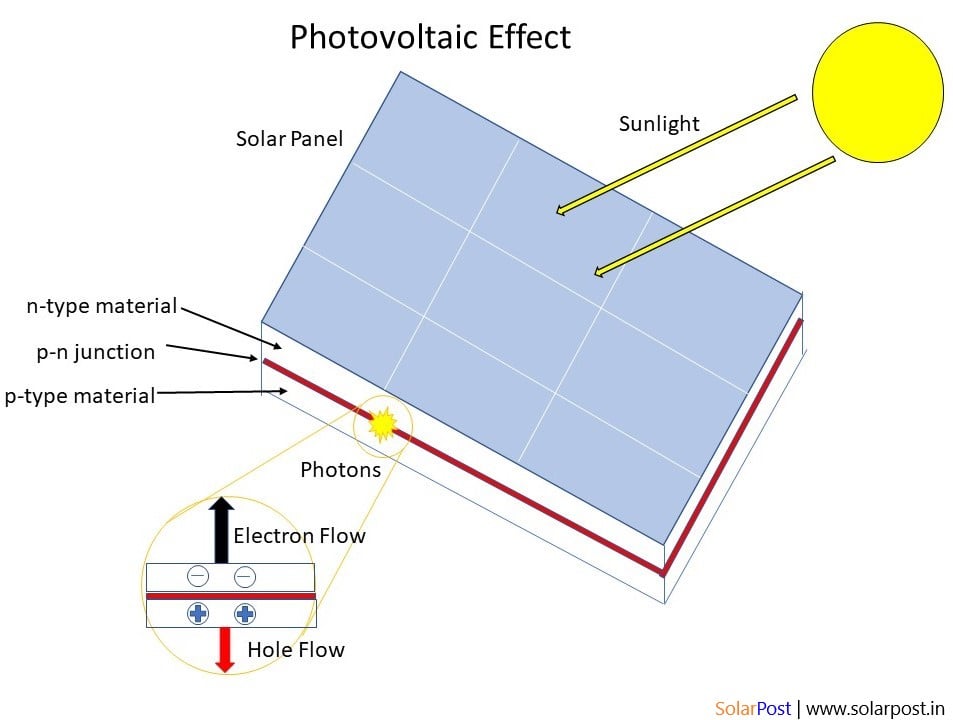
The Structure of a Photovoltaic Cell
A typical photovoltaic cell consists of several layers of materials, each with a specific function. The top layer is typically made from a transparent material that allows sunlight to pass through to the active layers below. Below the top layer is the semiconductor layer, which is responsible for absorbing the sunlight and releasing electrons. Finally, there is a conductive layer at the bottom of the cell to collect the electrons and transfer them to an external circuit.
How Photovoltaic Cells Work
When sunlight strikes the top layer of the photovoltaic cell, photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material, causing electrons to be released. These free electrons then move through the semiconductor material, creating an imbalance of charges that results in a flow of electricity. This flow of electricity can be captured and used to power electrical devices or stored in a battery for later use.
Advantages of Photovoltaic Cells
One of the main advantages of using photovoltaic cells to generate electricity is that they produce clean, renewable energy without any harmful emissions. Additionally, they can be used in remote locations where traditional power sources are not available, making them a popular choice for off-grid applications. Photovoltaic cells also have low maintenance requirements and can last for several decades, making them a cost-effective option for generating electricity.
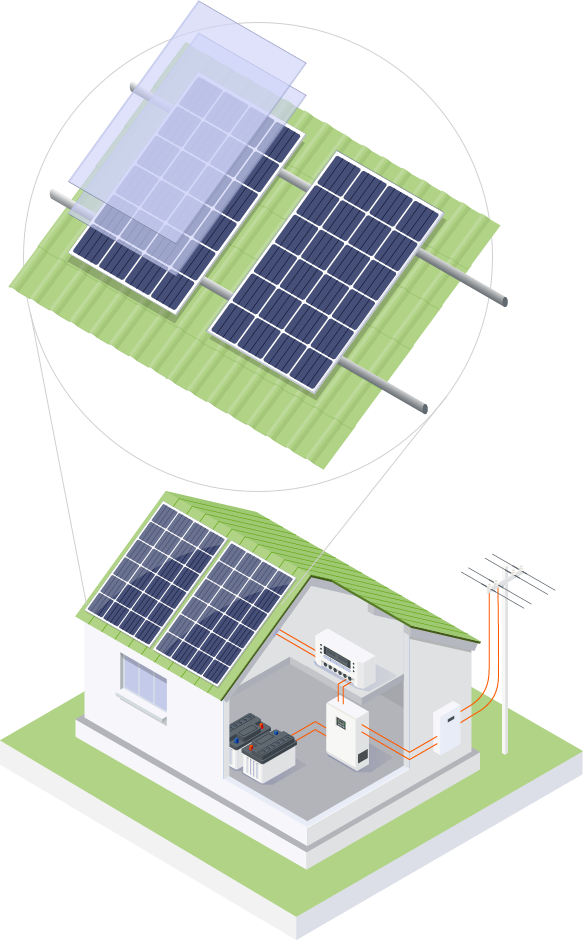
Applications of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are commonly used in solar panels to generate electricity for residential and commercial buildings. They are also used in solar-powered calculators, street lights, and other small-scale applications. In recent years, advancements in photovoltaic technology have led to the development of flexible and lightweight solar cells that can be integrated into building materials, clothing, and portable electronic devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells are a key technology for harnessing the power of sunlight to generate electricity. They offer a clean, renewable energy source that can be used in a wide range of applications. As technology continues to improve, photovoltaic cells are likely to play an increasingly important role in meeting the world’s energy needs in a sustainable manner.



