What is a photovoltaic cell and its uses

What is a photovoltaic cell
A photovoltaic cell, also known as a solar cell, is a semiconductor device that converts sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits the cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating a flow of electricity. The most common material used in photovoltaic cells is silicon, but other materials such as cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide are also used.
How does a photovoltaic cell work
Photovoltaic cells work based on the principle of the photovoltaic effect, where light is converted directly into electricity. When light strikes the cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating a flow of electricity. This electricity can then be used to power electrical devices or stored in batteries for later use. Photovoltaic cells can be connected in series or parallel to increase the voltage or current output, depending on the specific application.
Uses of a photovoltaic cell
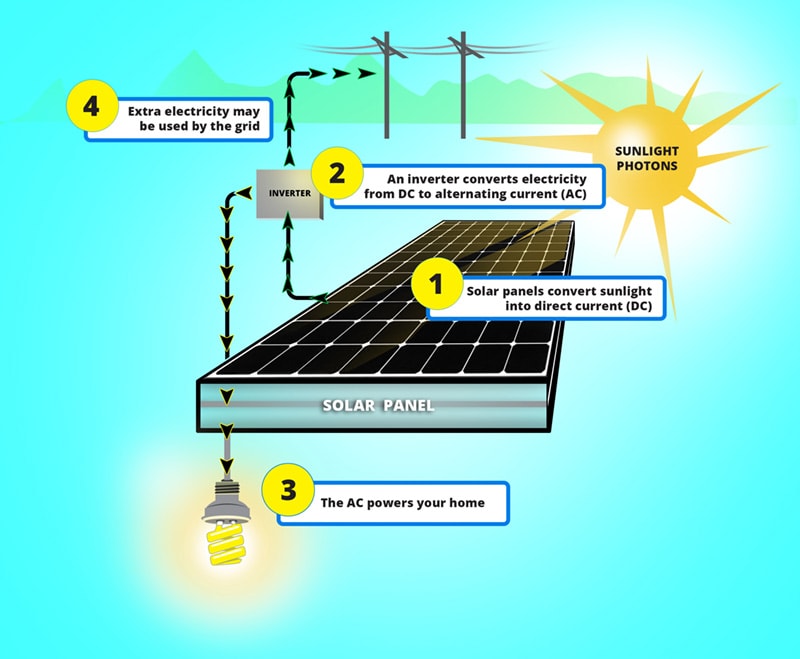
1. Solar panels
One of the most common uses of photovoltaic cells is in solar panels, which are used to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Solar panels are commonly used to provide power for homes, businesses, and even large-scale solar farms that generate electricity for the grid.
2. Portable chargers
Photovoltaic cells are also used in portable chargers for electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. These chargers contain small solar panels that can convert sunlight into electricity to recharge the devices’ batteries, providing a convenient and environmentally friendly way to keep devices powered on the go.
3. Space applications
Photovoltaic cells have been used in space applications for many years to power satellites and spacecraft. The cells are highly efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, making them ideal for use in the harsh environment of outer space where other power sources may not be feasible.
4. Rural electrification
In rural and off-grid areas where access to electricity is limited, photovoltaic cells are used to provide power for lighting, telecommunications, water pumping, and other basic energy needs. Solar home systems and microgrids powered by photovoltaic cells are an affordable and sustainable solution to bring electricity to remote communities.
5. Environmental benefits
Photovoltaic cells offer significant environmental benefits by producing clean, renewable energy without emissions of greenhouse gases or air pollutants. By harnessing the power of the sun, photovoltaic cells help reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to mitigating climate change.
In conclusion, photovoltaic cells play a crucial role in harnessing solar energy and converting it into electricity for a wide range of applications. With ongoing technological advancements and cost reductions, photovoltaic cells are increasingly becoming a key component of the global transition towards clean and sustainable energy sources.

