The photovoltaic effect is a phenomenon often used in the context of solar energy production. It refers to the process by which certain materials are able to convert light energy into electrical energy.

When light, in the form of photons, strikes a material such as a semiconductor, it can cause the material to release electrons, creating a flow of current. This is the basis for the operation of solar cells, which are used to capture and convert sunlight into usable electricity.
The photovoltaic effect was first observed in 1839 by French physicist Edmond Becquerel, and has since become the foundation for solar technology. By harnessing this effect, photovoltaic cells are able to generate clean and renewable energy from the sun, making them a vital component in the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
The effectiveness of the photovoltaic effect depends on the properties of the material used in the solar cell. Silicon is the most commonly used material due to its abundance and efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. Other materials, such as cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide, are also used in certain types of solar cells.
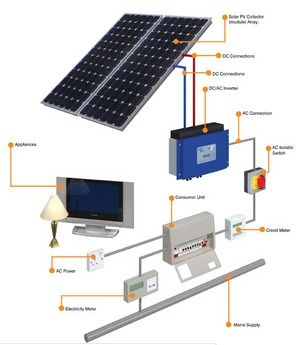
The photovoltaic effect has revolutionized the way we generate electricity, providing a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. As technology continues to improve, solar cells are becoming more efficient and affordable, making solar energy an increasingly viable option for meeting our energy needs.
In conclusion, the photovoltaic effect is the process by which certain materials are able to convert light energy into electrical energy. This phenomenon is the basis for the operation of solar cells, which play a crucial role in the generation of clean and renewable energy from the sun. As we continue to develop and improve solar technology, the potential for harnessing the power of the photovoltaic effect will only continue to grow. So let’s all make the most out of this amazing natural resource.

