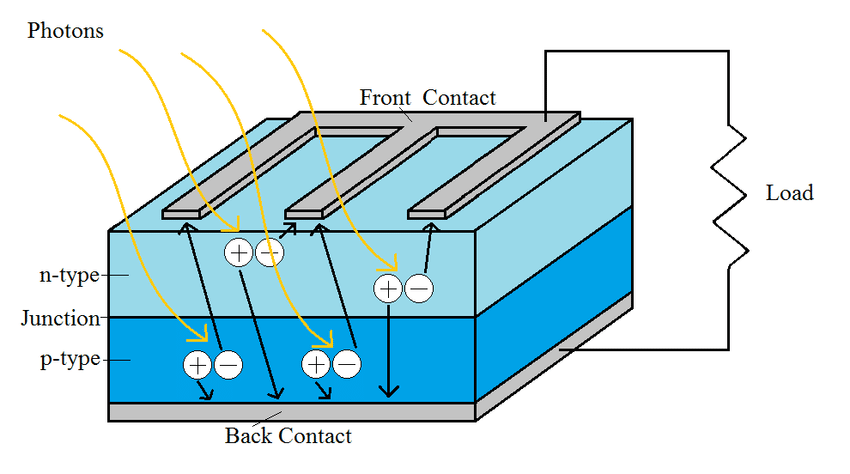
What Is a Photovoltaic Cell?
A photovoltaic cell, also known as a solar cell, is a device that converts light energy into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. This phenomenon occurs when certain materials, such as silicon, are exposed to light and generate an electric current as a result.
How Does a Photovoltaic Cell Work?
When light particles, or photons, strike the surface of a photovoltaic cell, they transfer their energy to the electrons in the material. This causes the electrons to become excited and move, creating an electrical current. This current can then be captured and used to power electrical devices or stored in a battery for later use.
Types of Photovoltaic Cells
There are several different types of photovoltaic cells, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film cells. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and environmental impact.
Applications of Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells are commonly used in solar panels to generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They can also be integrated into portable electronic devices, such as calculators and outdoor lighting systems, to provide a sustainable power source.
Benefits of Photovoltaic Cells
Using photovoltaic cells to harness solar energy offers numerous benefits, including reducing dependence on fossil fuels, lowering electricity bills, and minimizing carbon emissions. Additionally, photovoltaic systems require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan, making them a cost-effective and environmentally friendly energy solution.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic cells play a crucial role in the transition towards renewable energy sources. By converting sunlight into electricity, they offer a sustainable and clean power solution for various applications, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.