The Photovoltaic Effect: Generating Electricity from Light
What is the Photovoltaic Effect?
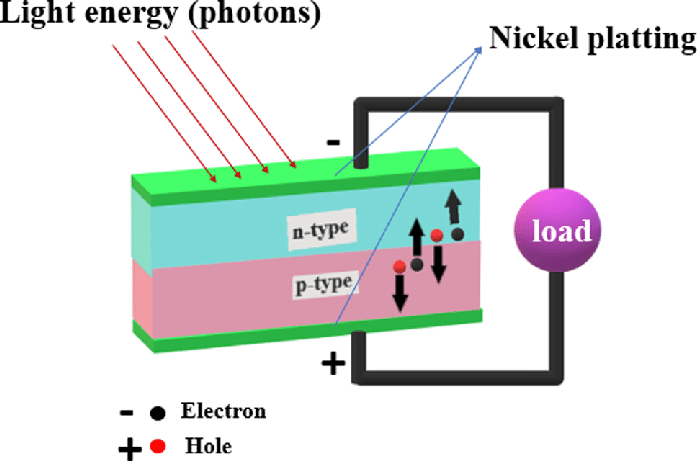
The photovoltaic effect is the process by which a material produces an electric current when exposed to light. This phenomenon is the basis for the operation of solar cells, which are used to convert sunlight into electricity. When photons of light strike the surface of a material, they can excite electrons, causing them to break free from their atoms and flow as an electric current. This process is the fundamental principle behind the generation of solar power.How Does the Photovoltaic Effect Work?
When light particles, or photons, strike the surface of a solar cell, they can transfer their energy to the electrons in the material. This causes the electrons to become free and mobile, creating an imbalance of charge within the material. By placing conductive contacts on the top and bottom of the solar cell, the free electrons can be collected and channeled into an external circuit, where they can do work, such as powering electrical devices or recharging a battery. This process allows for the direct conversion of sunlight into usable electricity.Applications of the Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect has revolutionized the way we generate electricity, offering a clean and renewable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. Solar panels, which are made up of interconnected solar cells, are used to harness the photovoltaic effect and convert sunlight into electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. The widespread adoption of solar power has also led to the development of off-grid systems, portable solar chargers, and solar-powered vehicles, further demonstrating the versatility and potential of the photovoltaic effect.

