Introduction to Photovoltaic Energy Conversion
Photovoltaic energy conversion, also known as solar energy conversion, is the process of converting sunlight into electricity. This technology is based on the photovoltaic effect, which occurs when certain materials generate an electric current in response to light exposure. Photovoltaic energy conversion has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its environmental benefits and the decreasing cost of solar panels.
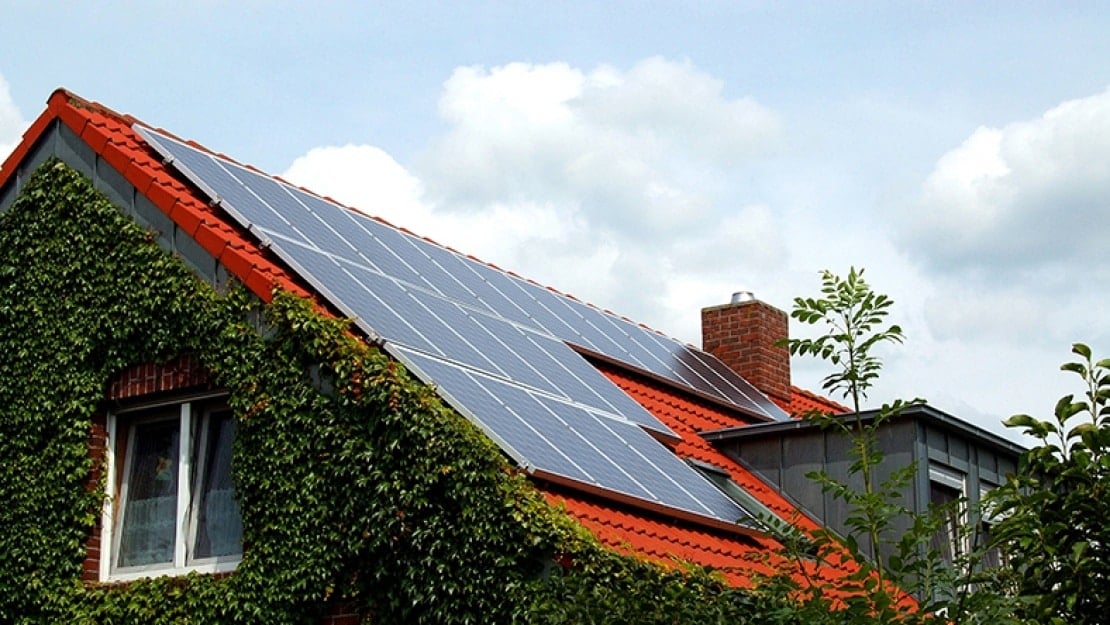

How Photovoltaic Energy Conversion Works
The Photovoltaic Effect
When sunlight hits a solar panel, it excites the electrons in the panel’s semiconductor material, causing them to flow and generate an electric current. This is known as the photovoltaic effect, and it is the basis for photovoltaic energy conversion.
Solar Cells
The basic building block of a photovoltaic system is the solar cell. Solar cells are made of semiconductor materials such as silicon, which are designed to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. Multiple solar cells are connected to form a solar panel, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities.
Efficiency and Output
The efficiency of a photovoltaic system is determined by the amount of sunlight it can convert into electricity. Factors such as the angle of the solar panel, the quality of the solar cells, and the weather conditions can all affect the system’s efficiency and output.
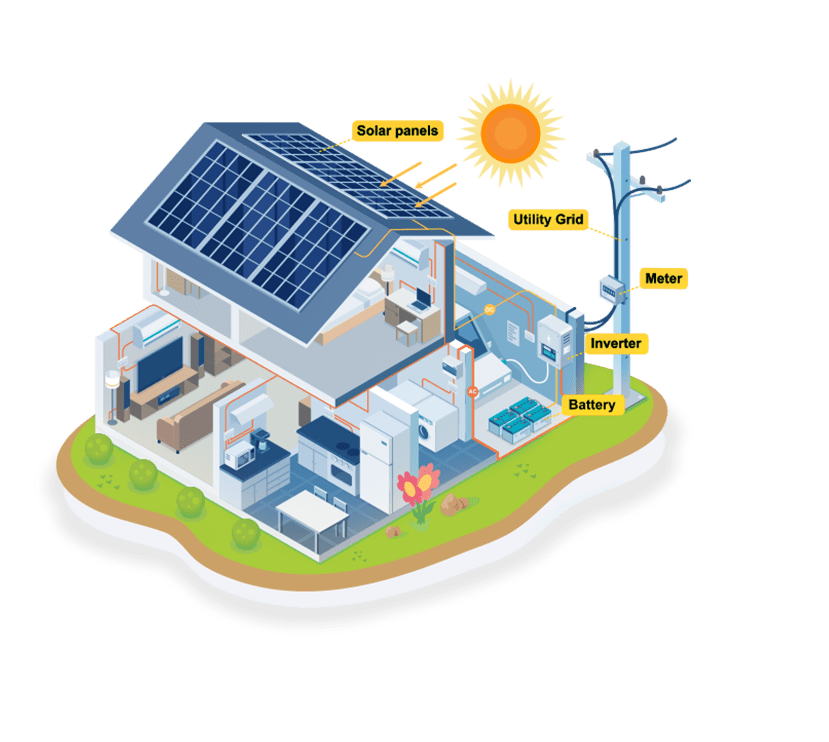
Applications of Photovoltaic Energy Conversion
Photovoltaic energy conversion has a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large-scale utility plants. Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, in open fields, or even integrated into building materials to provide clean and sustainable energy.
Residential Use
Many homeowners are choosing to install solar panels on their properties to reduce their reliance on traditional energy sources and lower their electricity bills. Residential photovoltaic systems can also earn homeowners tax credits and incentives for producing clean energy.
Commercial and Industrial Use
Businesses and industries are also adopting photovoltaic energy conversion to reduce their environmental impact and operating costs. Large-scale solar installations can power factories, warehouses, and office buildings, allowing companies to incorporate sustainable energy into their operations.
Grid-Tied Systems
Some photovoltaic systems are designed to be connected to the electrical grid, allowing excess energy to be sold back to utility companies. This not only provides a source of income for system owners but also contributes to the overall stability and sustainability of the electrical grid.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic energy conversion is a promising and rapidly growing technology that offers numerous benefits for both individuals and society as a whole. As the demand for clean energy continues to rise, photovoltaic systems are expected to play a crucial role in meeting our energy needs while reducing our environmental impact. With ongoing advancements in solar technology, the future of photovoltaic energy conversion looks bright.



