What is a Storage Battery and How Does it Work?
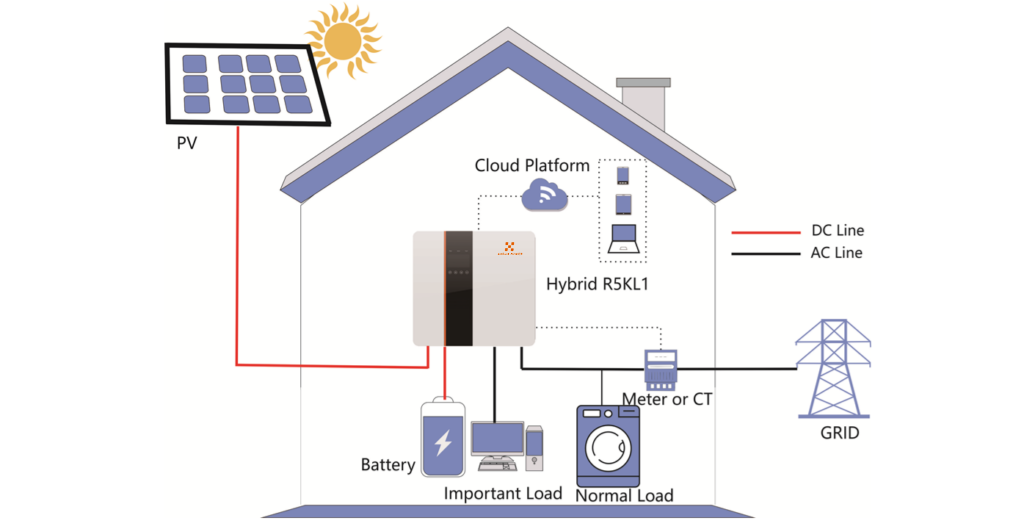
Introduction to Storage Batteries
Storage batteries, also known as rechargeable batteries or secondary cells, are a type of electrical battery that can be charged and discharged multiple times. They are widely used in various applications such as electric vehicles, uninterruptible power supplies, and renewable energy systems. Unlike primary batteries, which are designed for single use and then discarded, storage batteries are designed for repeated use and are an integral part of many modern technologies.
Types of Storage Batteries
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most widely used types of storage batteries. They are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications. Lead-acid batteries are relatively inexpensive and have a high energy density, but they are also heavy and have a relatively short lifespan compared to other types of storage batteries.

Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their high energy density, light weight, and long lifespan. They are commonly used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive than lead-acid batteries, but they offer significant performance advantages.
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are another type of storage battery that is commonly used in consumer electronics. They have a higher energy density and longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, but they are less commonly used in larger-scale applications due to their higher cost and lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries.
How Storage Batteries Work
Storage batteries work by converting chemical energy into electrical energy through a series of electrochemical reactions. When the battery is being charged, an electrical current is applied to the battery, causing the electrochemical reactions to occur in reverse, storing electrical energy in the battery. When the battery is being discharged, the electrochemical reactions occur in the opposite direction, releasing the stored electrical energy to power a device, vehicle, or system.
Charging and Discharging Process
During the charging process, the positive electrode of the battery (the cathode) accepts electrons from the external circuit, while the negative electrode (the anode) releases electrons to the external circuit. This causes the electrochemical reactions to store electrical energy in the battery. During the discharging process, the opposite occurs, with the cathode releasing electrons and the anode accepting electrons to power the external circuit.
Battery Management Systems
Many modern storage batteries are equipped with battery management systems (BMS) to monitor and control the charging and discharging process, as well as to protect the battery from overcharging, overdischarging, and other potential issues that could affect its performance and lifespan.
Conclusion
Storage batteries play a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from powering our electronic devices to storing energy from renewable sources. Understanding how storage batteries work and the different types available is essential for maximizing their performance and ensuring their safe and efficient use.


