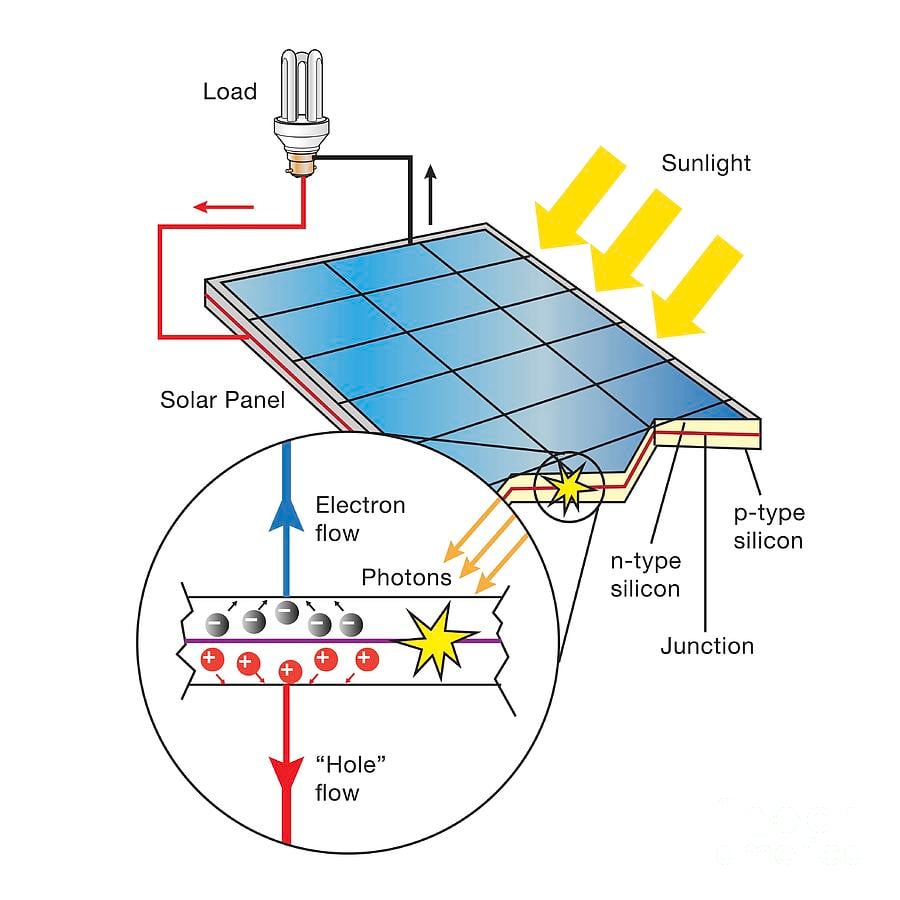
The active element in photovoltaic cells is the semiconducting material.
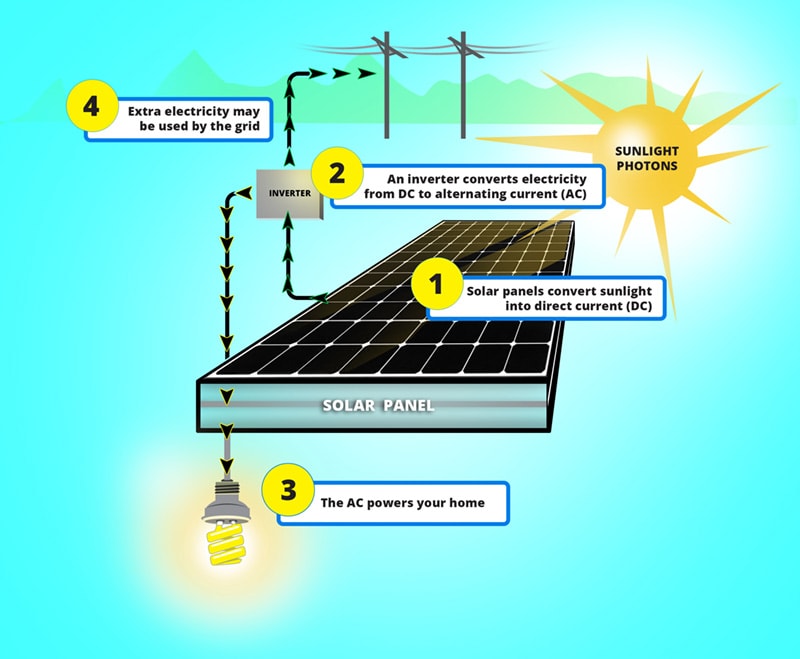
What is a photovoltaic cell?
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert light energy into electrical energy. They are the building blocks of solar panels and are widely used to capture sunlight and create clean, renewable energy.The active element in photovoltaic cells
The active element in photovoltaic cells is typically a semiconducting material, such as silicon. When photons from sunlight strike the surface of the cell, they knock electrons loose from the semiconducting material, creating a flow of electricity.Types of semiconducting materials
There are different types of semiconducting materials used in photovoltaic cells, including monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, and thin-film materials like cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide.