Photovoltaic systems are a popular and efficient way to generate electricity from sunlight. One key component of a photovoltaic system is the amp, or current, that is produced by the solar panels.
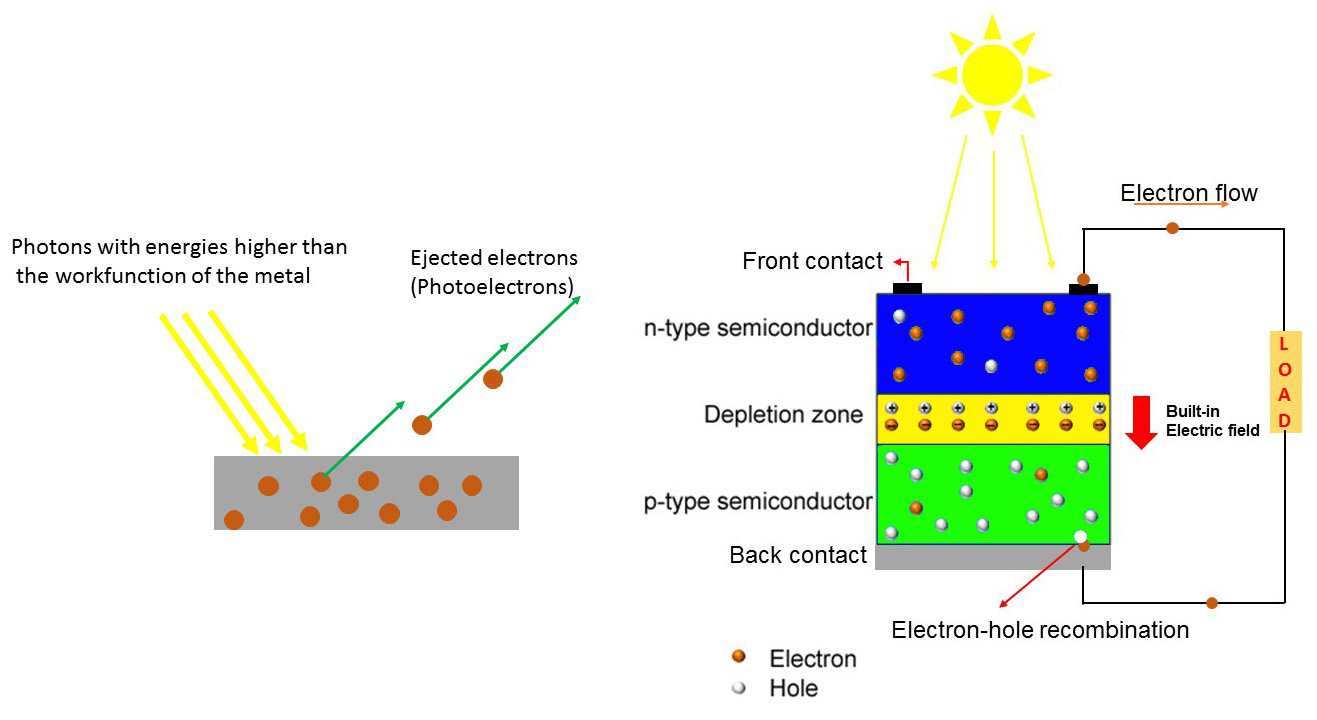
The amp of a photovoltaic system is a measure of the flow of electric charge through the system. It represents the rate at which electrons are moving through the solar cells to create a current. The higher the amp output of a photovoltaic system, the more electric charge is flowing, and the more power is being produced.
In a photovoltaic system, the amp output can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the size and efficiency of the solar panels, the angle and orientation of the panels, and the amount of sunlight that is hitting the panels. Generally, larger and more efficient panels will produce a higher amp output, as will panels that are positioned to capture the maximum amount of sunlight.
The amp output of a photovoltaic system is an important consideration when designing and installing a solar power system. It can impact the overall power output of the system and determine what types of equipment, such as inverters and batteries, are needed to manage and utilize the electricity that is being generated.

In conclusion, the amp of a photovoltaic system is a crucial factor in determining the overall power output of a solar power system. By understanding how the amp output is influenced and how it can impact system design, homeowners and businesses can make informed decisions about their photovoltaic installations. With the right design and configuration, a photovoltaic system can provide a reliable and sustainable source of electricity for years to come.

