The Difference Between Photovoltaic and Monocrystalline
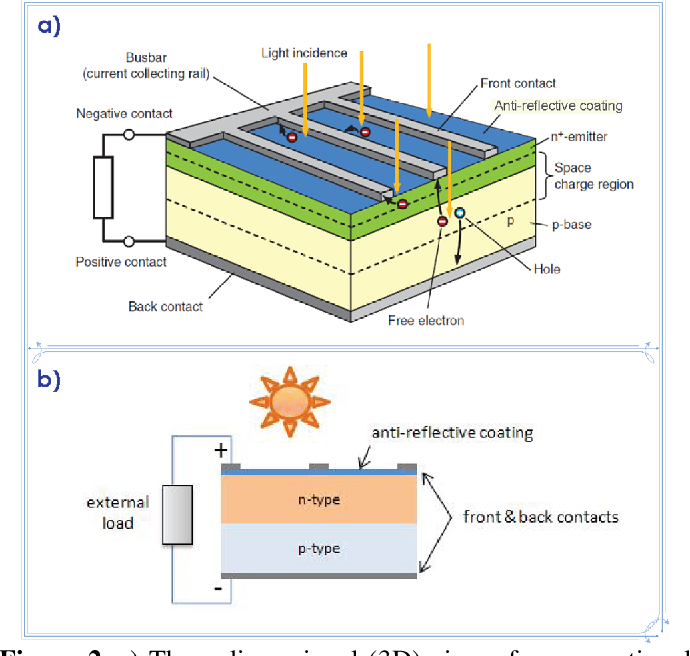
When it comes to solar energy, two commonly used terms are photovoltaic and monocrystalline. While they are often used interchangeably, there are some key differences between the two. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between photovoltaic and monocrystalline solar technology.
What is Photovoltaic Technology?
Photovoltaic technology, often abbreviated as PV, refers to the process of converting sunlight into electricity using solar cells. These cells are made from materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, where photons from the sunlight knock electrons free from atoms, generating a flow of electricity. Photovoltaic systems can be used to power everything from small electronic devices to large-scale power plants, making them a versatile and sustainable energy solution.
What is Monocrystalline Solar Technology?
Monocrystalline solar technology refers to the type of solar cell used in photovoltaic systems. These cells are made from a single crystal structure, typically silicon, which allows for greater efficiency and durability. The use of monocrystalline cells results in a higher power output and better performance in low-light conditions compared to other types of solar cells.
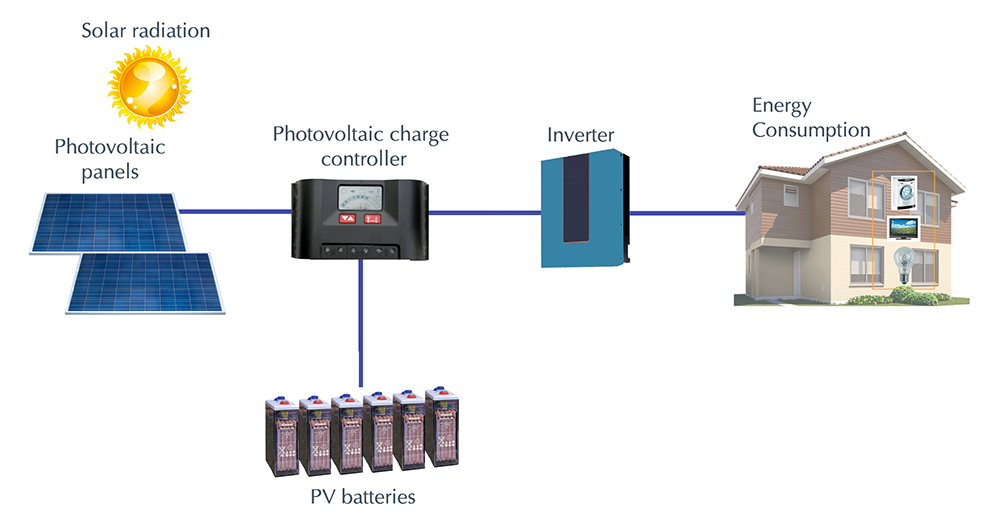
Efficiency
One of the main differences between photovoltaic and monocrystalline technology is their efficiency. Monocrystalline solar cells are known for their higher efficiency, typically ranging from 15% to 22%, compared to the 13% to 16% efficiency of traditional photovoltaic cells. This means that monocrystalline cells can generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, making them a more cost-effective option in the long run.
Durability
In terms of durability, monocrystalline solar cells also have an advantage over traditional photovoltaic cells. Their single crystal structure makes them more resistant to corrosion and wear, resulting in a longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements. This makes monocrystalline technology a more reliable choice for solar energy systems, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost
While monocrystalline technology offers greater efficiency and durability, it also comes at a higher cost. The manufacturing process for monocrystalline cells is more complex and resource-intensive, leading to higher upfront expenses compared to traditional photovoltaic cells. However, the long-term benefits of increased energy production and reduced maintenance costs often outweigh the initial investment for many consumers and businesses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both photovoltaic and monocrystalline technologies are used to harness solar energy, there are notable differences between the two. Monocrystalline technology offers higher efficiency, greater durability, and improved performance in low-light conditions, making it a popular choice for many solar energy applications. However, the higher cost of monocrystalline cells may be a limiting factor for some consumers. Ultimately, the decision between photovoltaic and monocrystalline technology will depend on individual energy needs, budget, and environmental considerations.



