< H1>Understanding the Difference between Photovoltaic Cells and Sunlight Cells< /H1> < H2>Overview of Photovoltaic Cells< /H2> Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity. These cells are made from semiconductor materials, typically crystalline silicon, and they work by capturing photons from sunlight and using them to create an electrical current. This process, known as the photovoltaic effect, is the foundation of solar energy technology and is widely used in photovoltaic panels for generating electricity.
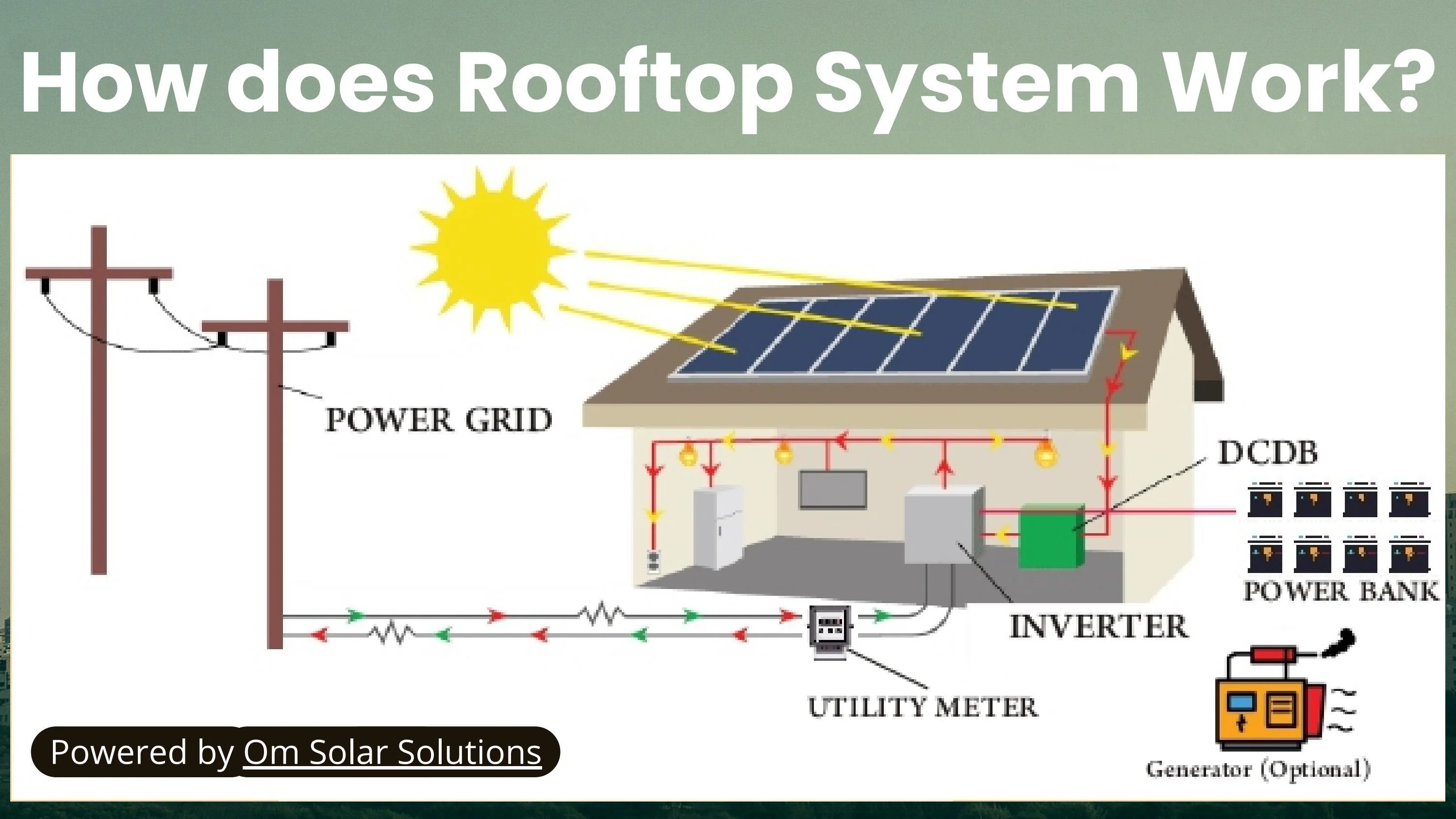
< H2>Overview of Sunlight Cells< /H2> Sunlight cells, on the other hand, are specialized in capturing sunlight and converting it into heat, which can then be used for various applications such as heating water or air. These cells are commonly made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, and are designed to absorb as much sunlight as possible to generate heat.
< H2>Differences between Photovoltaic Cells and Sunlight Cells< /H2> < H3>Functionality< /H3> The primary difference between photovoltaic cells and sunlight cells lies in their functionality. Photovoltaic cells are designed to convert sunlight into electricity, while sunlight cells are designed to convert sunlight into heat.
< H3>Materials< /H3> Another key difference is the materials used in the construction of these cells. Photovoltaic cells are typically made from semiconductor materials such as silicon, while sunlight cells are made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum.

< H3>Applications< /H3> Finally, these cells are used for different applications. Photovoltaic cells are primarily used in solar panels to generate electricity for residential, commercial, and industrial use, while sunlight cells are used in solar thermal systems for heating water, air, or other fluids.
< H3>Efficiency< /H3> In terms of efficiency, photovoltaic cells are more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity, with modern cells achieving efficiencies of around 20-25%. Sunlight cells, on the other hand, are designed to maximize heat generation and are less efficient at converting sunlight into electricity.
< H3>Conclusion< /H3> In conclusion, while both photovoltaic cells and sunlight cells harness the power of sunlight, they serve different purposes and operate on different principles. Photovoltaic cells are focused on converting sunlight into electricity for various applications, while sunlight cells are designed to capture and convert sunlight into heat. Understanding the differences between these two types of cells can help in choosing the right technology for specific energy needs.

